Current page: 4 (the book has a total of 18 pages) [available reading excerpt: 10 pages]
1. What makes it possible to combine such dissimilar animals into one type?
2. Are there echinoderms in your area?
General characteristics. To type echinoderms, numbering more than 6500 species, includes animals that live in the seas and oceans, both at great depths and in shallow waters.
The body of echinoderms, from 5 mm to 5 m long, has radial (radial) symmetry, lime skeleton, often with numerous needles, spines, etc. All echinoderms have water vascular system, with the help of which they can move, and representatives of some species can touch and even breathe. Slow movement along the bottom is carried out when the tubule legs are filled with liquid, often with suction cups at the ends. The body shape of echinoderms is very diverse. There is no division of the body into sections. Echinoderms are usually dioecious. They have a high ability to regenerate.
Rice. 35. Classes of echinoderms: sea lilies - 1, 2; starfish - 3, 4, 5; sea urchins - 6, 7; holothurians - 8
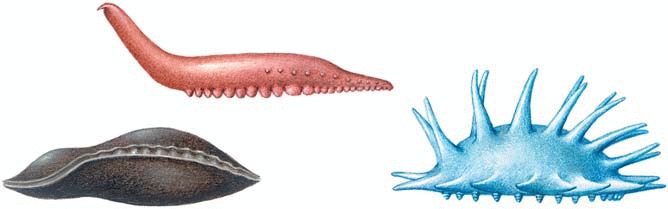
Rice. 36. Holothurians
Class Sea lilies(Fig. 35). Among sea lilies there are sessile and free-floating forms. The mouth opening of these echinoderms opens at the top of the body. All crinoids feed on small planktonic organisms. Breathe on the surface of the body. There are usually 5 tentacles, but they can branch up to 200 or more processes.
Starfish class(Fig. 35). These are sedentary animals with 5 to 50 rays. Their mouth opening is on the underside of the body. Starfish feed mainly on dead animals, as well as silt and sedentary animals. Some predatory starfish destroy commercial molluscs. The stomach of these echinoderms can turn out through the mouth opening and envelop the prey.
Among starfish there are both hermaphrodites and dioecious ones. Reproduction is asexual and sexual.
The fecundity of sea stars can be different: from a few dozen to 200 million eggs per individual. In the shallow waters of the northern seas, starfish freeze in winter and thaw in spring.
Class Sea urchins(Fig. 35). Free-moving animals with a hard shell covered with movable spines. Representatives of some species can use them to move along the bottom. The mouth is equipped with a gnawing apparatus and is located on the underside of the body. They feed on algae, sedentary animals, silt. One female spawns up to 20 million eggs.

Rice. 37. Ophiurs
In some species of sea urchins, care for offspring is observed: they bear eggs and juveniles on the body.
Class Holothuria, or Sea cucumbers(Fig. 35, 36). The body of these animals shrinks strongly when touched and becomes like a cucumber. related to holothurians trepangs edible, they are caught and even specially bred. The body length of holothurians is usually from a few millimeters to 2 m. The mouth is located at the anterior end of the elongated body. Holothurians feed mainly on animals that live on the surface of the silt, plants and their remains.
Almost all holothurians have separate sexes, but there are hermaphrodites. Some species of these echinoderms take care of their offspring. One female spawns up to 77 million eggs.
Holothurians live in the seas at various depths and are not very sensitive to salinity. An amazing feature of them is their adaptability to protection from enemies and other dangers. Strongly shrinking, holothurians throw out their insides through the anus, which are subsequently restored.
Ophiura class(Fig. 37). Flat, free-moving echinoderms, up to 10 cm in diameter and with long, sometimes branching rays. The brittle stars move, lifting the body above the ground with the help of rays. Stretching branched rays, brittle stars catch and capture, filtering water, small planktonic organisms.
Ophiurs are mostly dioecious, but there are also hermaphrodites and reproduce asexually.
There are brittle stars living on other echinoderms (hedgehogs, lilies), as well as on sponges and corals. Some of the ophiuroids can glow. Many have developed the ability to regenerate.
Water-vascular system. Lime skeleton.
Questions
1. Why were echinoderms able to populate all the seas and oceans at depths and shallow waters?
2. On what grounds did echinoderms get their name?
3. What is the meaning of echinoderms?
4. Which of the previously studied animals had radial (radial) symmetry?
Tasks
Using various sources of information, prepare a report about the representatives of the Echinoderm type that are of interest to you.
Do you know that…
Echinoderms are capable of regeneration after self-mutilation of tentacles and rays.
Trepang meat contains 100 times more iodine than any other marine invertebrate, and 10,000 times more than beef. In addition, the body of trepangs contains chlorine and sulfur, phosphorus and calcium, manganese and magnesium, cobalt and many other elements necessary for the human body for normal development.
Starfish are long-lived among echinoderms: they live up to 20 years. Some of them can survive after starving for up to 1.5 years or freezing in shallow water.
1. Is there a similarity between arthropods and previously studied animals?
2. What arthropods live in your area?
General characteristics. The name of the type is given for the characteristic articulation of the legs of its representatives. The type of arthropods is the most numerous in the animal world: it includes 2/3 of all species of creatures living on Earth. Representatives of the type are bilaterally symmetrical animals that have mastered all the living environments of the biosphere: from the depths of the ocean to the stratosphere, from pole to pole. They swim, crawl, jump, run, fly, dig, build.
The outer cover of arthropods is impregnated with a special organic substance - chitin(see fig. 144). After hardening, chitin does not allow the animal to grow, and its growth is carried out only during periods of molting, when the body is deprived of a protective cover. The number of lines is different. Arthropods have well-developed organs of vision, smell, balance, touch, and some have hearing. Arthropods are dioecious (only individuals of a few species are hermaphrodites). Development can take place with or without transformation (Fig. 38).
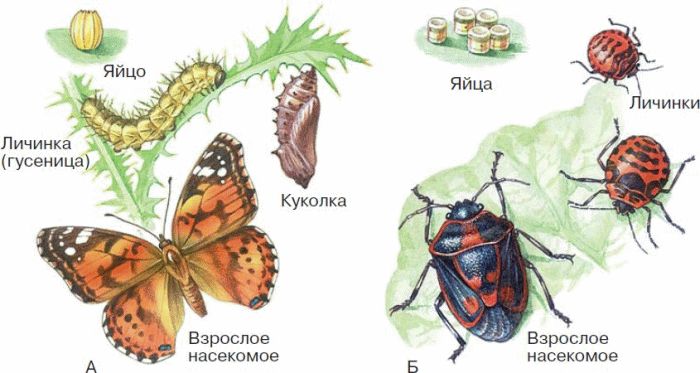
Rice. 38. Development of insects: A - with transformation; B - without transformation
Class Crustacea(Fig. 39). These are mainly marine animals, representatives of a number of species live in fresh waters and on land. Body length from 0.1 mm to 80 cm. Maximum weight up to 20 kg.
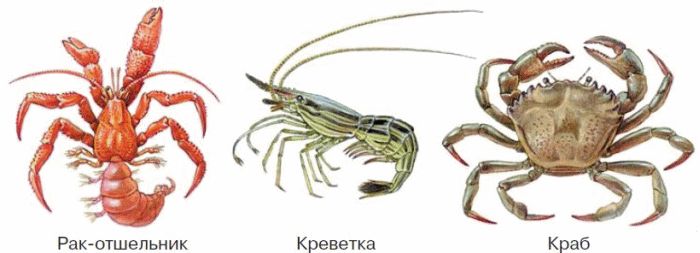
Rice. 39. Representatives of decapods
The number of body sections is different, but in many it is possible to distinguish the head, chest and abdomen. Often parts of the body grow together to form cephalothorax, such as crabs.
The sense organs are well developed: touch, smell, balance, hearing, vision. complex eyes, consisting of a large number of simple eyes - facets, each of which sees only part of the object. The general view of the object is formed as in a mosaic. This vision is called mosaic, and eyes faceted.
Many crustaceans are used by humans for food, among them shrimps, crabs, lobsters, lobsters, crayfish.
Most crustaceans are dioecious. Males, as a rule, differ from females: in some species they are larger, in others they are smaller.
Lab #5
Introduction to crustaceans
Equipment:
hand magnifier, microscope, glass slides, pipettes; cultures of daphnia, cyclops, shell crustaceans; wet preparations: crayfish, shrimp, etc.
Progress:
1. Examine live crustaceans in test tubes with a magnifying glass. Note their size, color, nature of movement in the water.
2. Place several cultured animals in turn in a drop of water and examine them under a low magnification microscope. Note the similarities and differences in the external structure of the body, in characteristic movements, color.
3. Compare large crustaceans: shrimp and crayfish. Identify the similarities and differences in the external structure.
4. Justify the conclusion that the studied crustaceans belong to the same class in the phylum Arthropoda.
Class Arachnids(Fig. 40–44). Mostly terrestrial species belong to this class. All arachnids have four pairs of walking legs. Arachnids are predators that attack other animals. For these purposes, they have various devices: from poisonous glands to spider web warts for making trapping nets. The body length of arachnids is from 0.1 mm to 12 cm.
Currently, more than 62 thousand species of arachnids are known. These include scorpions, harvestmen, ticks, spiders and other members of the class. Some of them, such as scorpions, are very ancient animals (Fig. 41).
scorpions live in countries with a warm or hot climate, from deserts to humid forests, sometimes found in the mountains. In Russia, scorpions live in the lower reaches of the Volga, in the Caucasus. Scorpions hunt at night. By secreting poison, scorpions immobilize prey or kill it. They feed on various arachnids, lizards or mouse-like rodents. Scorpions can starve up to 1.5 years. For humans, they are also very dangerous.
Females often give birth to live cubs, but some scorpions lay eggs with already formed embryos.
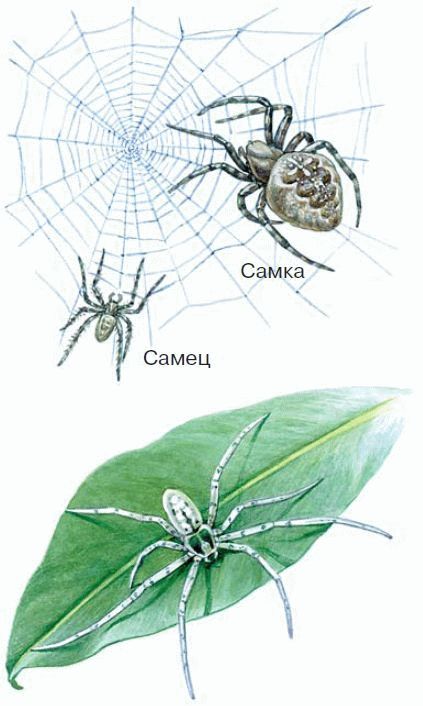
Rice. 40. Spiders

Rice. 41. Scorpio
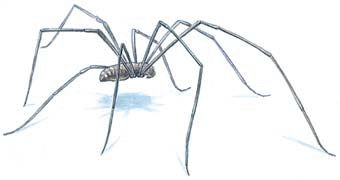
Rice. 42. Harvester
haymakers- another group of arachnids (Fig. 42). Their long legs can easily come off, while their owner successfully escapes at this time. Haymakers are widespread everywhere. They lead an active lifestyle in search of food. They feed on small molluscs, arthropods, including insects. Do not refuse the rotting remains of animals and plants. During reproduction, harvestmen lay from several tens to several hundred eggs.
Ticks- a large group of arachnids, in which all parts of the body are, as it were, merged (Fig. 43, 44). It is assumed that there are several hundred species of ticks. They live almost everywhere: from the polar regions to the equator, in the depths of the sea, in underground sources, in the soil, etc.
Once on the skin of animals or humans, blood-sucking mites damage it and feed on blood. The body of mites can become very large. To remove a tick that has stuck to it from the skin, it must be lubricated with vegetable oil, blocking the access of air, and slightly rocked until its head is released from the skin. If this is not done immediately, then the head can very easily come off and the wound will become inflamed. dangerous to humans and scabies mite- the causative agent of scabies (Fig. 44).
It damages human skin. In it, the tick gnaws a passage and lays eggs there. This usually occurs in the folds of the body where the skin is softer, such as on the hands. Scabies mites are easily transmitted from person to person. Herbivorous mites damage stocks of grain, flour and bread. Some feed on plant sap. Their dimensions are 0.2–0.5 mm.
The development of ticks depends on many environmental factors and can occur on one, two or three hosts. This allows ticks to survive in the most adverse conditions and quickly restore their numbers.
Spiders represent the largest group of arachnids. Spiders have populated all the land, and there is hardly a place where they would not be. Spiders are very ancient animals, they are considered one of the first settlers among land arthropods. The sizes of spiders are different: the body length is from 0.8 mm to 12 cm. The color is varied, often masking the body of the spider in its habitat.
All spiders have spider warts And glands. Web used for building trapping nets And cocoon for eggs, distribution of young spiders, making a shelter and wintering bag. Spider thread is very strong. Among spiders there are stray and sedentary. Spiders feed on various insects, some eat earthworms, snails, ants, lizards, frogs, mice, birds, tadpoles, small fish.
The digestive system of spiders is interesting because digestion carried out outside the body. After catching prey, the spider introduces into its body the secret of poisonous glands, which simultaneously serves as digestive juice. After some time, the spider absorbs the digested, liquid food, and it enters the stomach, then into the intestines.
The breath of spiders is provided lung sacs And trachea(see fig. 157). The circulatory system is open, has a pulsating dorsal vessel. The blood is colorless. The nervous system consists of a well-developed supraglottic ganglion and the abdominal chain.
Arachnids have separate sexes. Fertilization in representatives of some species is external, in others it is internal. They occur in reproduction without fertilization, when the female lays unfertilized eggs, from which only females develop. This phenomenon is called parthenogenesis. Usually arachnids lay eggs, but there are also viviparous ones. In laying from one to 30 thousand eggs. Development without transformation the eggs hatch into small adults that look like adults. In many species, care for offspring is observed: females guard the cocoon with eggs.
It is not uncommon for a female spider to eat a male after mating if he does not have time to escape.
Rice. 43. Ticks

Rice. 44. Scabies mite
Chitin. Complex eyes. Mosaic vision. Development without transformation. Spider warts. The web is a trapping net. Lung sacs and trachea. Parthenogenesis.
Questions
1. What features of the structure of arthropods allowed them to settle almost all over the planet?
2. On the basis of what can it be argued that crustaceans and spiders belong to the same type?
4. What is the importance of crustaceans and arachnids in nature and human life?
5. What is common in the digestion of food between starfish and spiders?
6. Using various sources of information, answer the question: why does the spider itself not stick to its web?
Do you know that…
A tick can live without food for about 6 years.
From the cobwebs, they have long tried to weave fabrics. At the beginning of the XVIII century. in France, gloves and stockings were made from such fabric; in China, the web fabric was called the "fabric of the eastern sea", it was very light, beautiful and durable.
The venom of the karakurt spider is 15 times stronger than the venom of a rattlesnake.
Among spiders, there is the only species that has mastered the aquatic habitat - the silver spider. It lives in the fresh waters of Europe among aquatic plants and feeds on aquatic arthropods. The supply of air for breathing in this water spider is held by numerous hairs on the abdomen. The female builds a bell-shaped underwater nest (with air supply) from the web, in which she places a cocoon with eggs and guards them until the juveniles emerge.
1. What insects live next to a person?
2. How does a person use insects?
General characteristics. Insects got their name for the characteristic notches on the abdomen. This is the largest group of animals, numbering about 1.5 million species.
Unlike crustaceans and arachnids, insects have 3 pairs of legs, and the body is clearly divided into head, thorax and abdomen.
Insects are very resistant to adverse environmental conditions: some survive even after freezing at a temperature of -30 ° C, others live in hot springs at temperatures up to +50 ° C.
The size of insects is very different: the smallest are less than 0.25 mm long, and the largest are up to 30 cm.
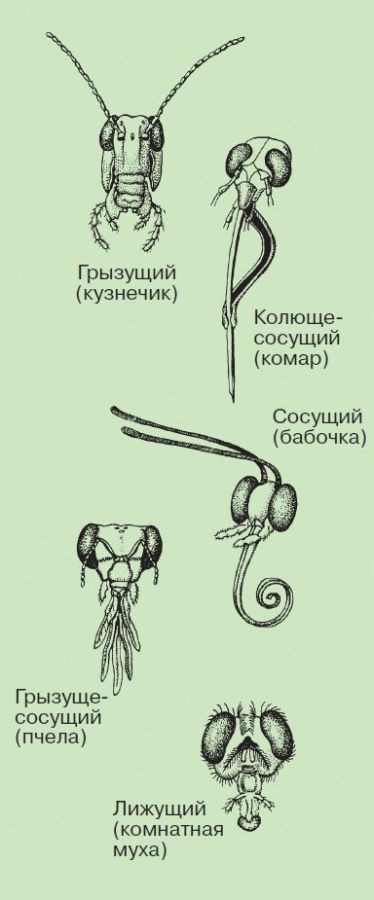
Rice. 45. Insect mouthparts
Social insects live in communities: for example, bees- 40-80 thousand individuals, ants- 500-600 thousand each, and termites- up to 3 million individuals.
The physical strength of insects does not match their size. So, an ant can pull a load 500 times heavier than its own weight, and a bee - 300 times.
The ability to fly provided insects with a wide distribution around the planet, the ability to find marriage partners over a large area, evade enemies, and catch prey.
The food of insects is very diverse, and in species adapted to eating certain foods, the oral apparatus has a certain structure. It can be sucking, like butterflies, licking, like flies, gnawing, like beetles or grasshoppers, piercing-sucking, like mosquitoes and bedbugs (Fig. 45).
There are insects that feed on seemingly completely inedible substances, such as wax, wool, bone or horn matter, feathers, wood, and dung.
In social insects, "agricultural production" can be observed. Many ants, for example, breed and disperse aphids to obtain honeydew, and also eat them, providing themselves with protein food (Fig. 46). In addition to aphids, ants use mealybugs, psyllids, cicadas, and caterpillars as "livestock".
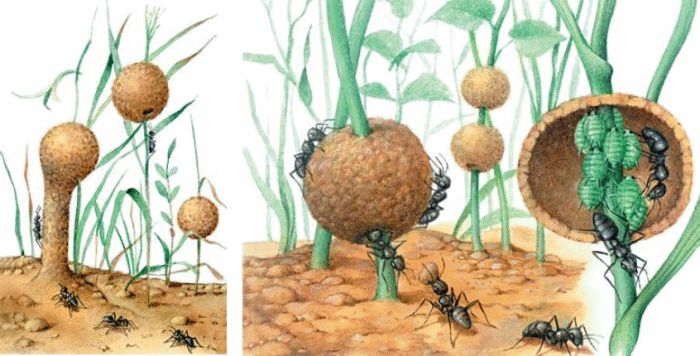
Rice. 46. Animal Farms
Among insects, there are domesticated species - these are honey bee And mulberry silkworm.
An important feature underlying the taxonomy of insects is the structure and number of wings, as well as the structure of the oral apparatus.
Lab #6
The study of representatives of insect orders
Equipment:
collections of insects of various orders, collections of insect pests of the forest, garden, vegetable garden, food stocks and others available at the school.
Progress:
1. Consider the proposed collections.
Identify the similarities and differences between individual insects, paying attention to their size, body shape, color, location and number of wings, antennae, eyes.
Note what their local names are, what is their significance in nature and human life.
2. Make a list of the names of insect species from the collection related to each order. Complete it with a list of local species that you know well.
3. Consider pests of various crops or food supplies. Note the nature of the damage they cause. Remember if you have seen such damage or such insects in nature.
Insects.
Questions
1. Why are insects very interesting as objects of study?
2. What social insects are found in your area?
3. What pests did you know before?
Tasks
Using various sources of information, prepare a report on insects that can come back to life after freezing and those that can live in hot springs.
Why does a person chase cockroaches, but does not pay attention to mayflies?
cockroach- mostly nocturnal animals, resting during the day in various secluded, inaccessible places (Fig. 47). They love moisture and warmth: the drier and cooler the climate, the fewer of them. Their size is different - from 2 mm to 12 cm. Among the approximately 3.5 thousand species living now, only 6 live in a human dwelling. The cockroaches include very ancient insects, and all of them could fly before. The cooling of the climate led to the fact that many species died, and some lost the ability to fly, having mastered new habitats, for example, in people's apartments.
cockroaches omnivorous, eat plant foods, including wood, at home can damage paper, book bindings, leather products. The oral apparatus is gnawing. Cockroaches run pretty fast - up to 70 cm per second.
Development without complete transformation. The larvae are similar to adult insects, they grow during molts. They live for about a year and a half.
To Orthoptera refer grasshoppers, filly, crickets, bear and other representatives (Fig. 48). There are more than 20 thousand species of them. Orthoptera are distributed from the Arctic Circle to the tropics. Characteristic features are large hind legs adapted for jumping and elongated straight narrow front wings, turned into elytra and protecting fan-shaped hind wings. The body is elongated, the mouth apparatus is gnawing. Large eyes and antennae, short or long. Orthoptera emit a variety of sound signals by which it is easy to distinguish them. The auditory apparatus of grasshoppers is located on the shins of the front legs; in locusts - on the sides of the first segment of the abdomen.

Rice. 47. Cockroach
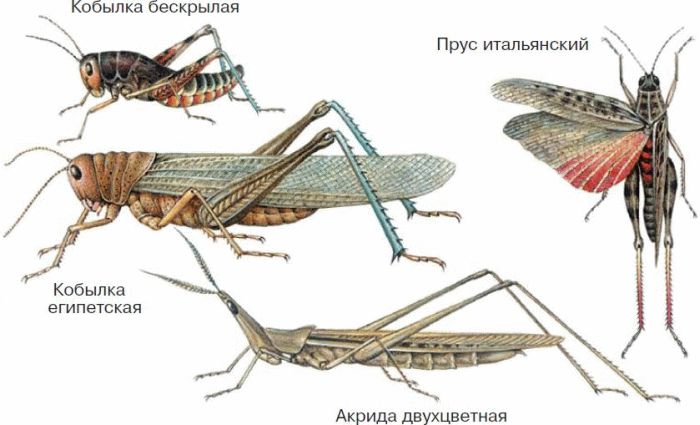
Rice. 48. Orthoptera
Female orthoptera have on the abdomen ovipositor. Eggs are laid in the ground, on the surface of plants, or inside plant organs.
Development without complete transformation. The larvae are similar to adult insects. Some Orthopterans feed only on other insects or plant and animal food.
Grasshoppers, insects, well known to all, live in the forest, forest-steppe, steppe and semi-desert regions of our country. Most of them are found in tropical and subtropical countries.
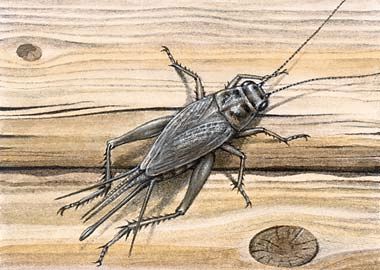
Rice. 49. Cricket

Rice. 50. Medvedka
crickets are black, straw-yellow, brown. Crickets live in earthen burrows or under stones (Fig. 49). They lead mainly a nocturnal lifestyle. They usually eat plant foods. The chirring of crickets occurs, as in grasshoppers, due to the friction of the front wings against each other.
Crickets defend their territory by driving other crickets away from it. Crickets hibernate in dug burrows up to 70 cm deep, some species hibernate in anthills.
Filly And locust differ in lifestyle. Fillies do not form huge flocks. Locusts gather in flocks and are very harmful to agriculture, for which they received the name "Egyptian execution". Huge flocks can fly up to 2400 km. When they land on the fields of agricultural plants, they leave behind a desert. The number of individuals in a flock can reach more than 35 billion. Locust control is carried out using chemical methods of protection.
Medvedki lead an underground lifestyle (Fig. 50). They are superbly adapted for digging with their forelimbs, easily creating complex underground systems of passages. They swim, dive and even fly (at night) very well. Under the ground, they move both forward and backward. Medvedki harm garden plants, damaging their root system. They settle mainly in meadows and vegetable gardens, they love floodplains of rivers.
earwigs are fairly common insects. The body length of earwigs is from 4 to 78 mm. At the end of the body of earwigs there are outgrowths, for which they are sometimes called "two-tails" (Fig. 51). These outgrowths perform the function of defense and attack.
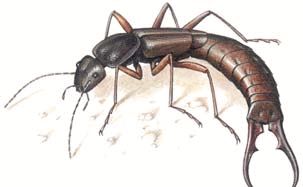
Rice. 51. Earwig
More than 1,700 species are known, but in our country there are about 20. Most of the species are confined to tropical countries.
Earwigs lead a hidden lifestyle, active at night, during the day they hide under stones, tree bark, and in other secluded places. They feed on dead and living plants, fungi, algae, and insects. They often harm plants by eating leaves, shoots, flowers, and immature seeds.
Earwigs lay their eggs in clusters in earthen passages in autumn and spring. The female hibernates with her eggs and guards them. Development with incomplete transformation. Earwigs can fly, especially intensively during breeding.
Mayflies distributed almost all over the world. Adult individuals have transparent delicate wings, and at the end of the abdomen there are 2–3 thin tail filaments (Fig. 52). In adulthood, they live one or more days, for which they received this name. Adults do not feed, their task is to mate and leave offspring. Eggs are laid in water, larvae develop in the same place.
Mayfly larvae are found in fast streams and rivers, in stagnant reservoirs. They dig in the mud, crawl or attach themselves to underwater objects, feed on dead plants and animals, and have predators. The larval state lasts 2–3 years. At this time, they are sensitive to water pollution and, if there are a lot of chemicals, the number of larvae is sharply reduced. The exit from the water is massive. The larvae serve as good food for fish. About 1500 species are known. Sizes from 1 to 6 cm.
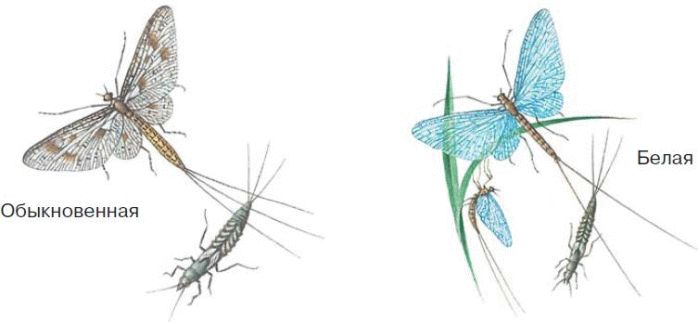
Rice. 52. Mayflies
cockroach. Orthoptera. Earwigs. Mayflies.
Questions
1. In connection with what did the orthopterans get their name?
2. What role do orthopterans play in nature?
3. Why is a bear compared to a mole?
4. What is the importance of earwigs in nature and human economy?
5. Why don't mayflies eat as adults?
Tasks
Using various sources of information, prepare a report on the lifestyle of Orthoptera and the signs associated with them.
Do you know that…
Cockroaches do not tolerate cold: at -5 ° C they die after 30 minutes, and at -7 ° C - after 1 minute.
Cockroaches are very ancient insects: their fossil ancestors are known, who lived 300–400 million years ago.
Locusts serve as a favorite type of food not only for carnivores, but even for herbivores. Sheep, horses, antelopes, elephants eat it in large quantities.
