Autumn is one of the most beautiful seasons of the year. The diversity and richness of nature during this period simply amaze the mind, the simple and complex leaves are so different from each other. The leaf arrangement of each plant is special (it can be alternate or whorled), and it is from it that one can determine which species it belongs to. Let's take a closer look at the features and functions of each type of leaf.
Definition in botany
Along with flowers, roots, stems and shoots, leaves are the most important vegetative organs in plants, which are also responsible for the function of photosynthesis. In addition, they perform many other tasks, for example, they are involved in the processes of respiration, evaporation and guttation of plants. There are the following simple and complex, each of them has its own characteristics and is found in a certain type of plant.
Very often, leaf blades are mistaken for leaves, but in fact it is an organ that consists of a blade (veins pass through it) and a cutting that originates at the base and connects the leaf blade with stipules. It always occupies a lateral position on the stem, and all the leaves are arranged on it in a certain sequence in such a way as to provide optimal access to the sun's rays. Its size can vary from 2 cm to 20 m (for tropical palms).
External structure and forms
One of the features of these organs is their flat shape, which ensures maximum contact of the plant surface with the air and sunlight. The forms are simple and differ from each other in appearance. Simple ones have only one leaf blade, which is connected to the base with the help of a petiole. Complex ones consist of several leaf blades located on one petiole. Remember what the thickest vein looks like in the middle, to which two or three stipules are attached on each side. Such a complex is called opposite, because the leaf blades are located symmetrically to each other.
The main components are the plates and veins that run along their surface, as well as the petiole, stipules (although not all plants have them) and the base, with which the element is connected to the stem of a tree or other plant.
Unlike the shape of a simple sheet, in complex ones you can find several varieties that have their own distinctive properties and features.
Internal structure
The upper surface of the leaf blades is always covered with a skin, which consists of a layer of colorless cells of the integumentary tissue - the epidermis. The main functions of the skin are protection from external mechanical damage and heat transfer. Due to the fact that its cells are transparent, sunlight passes through it unhindered.
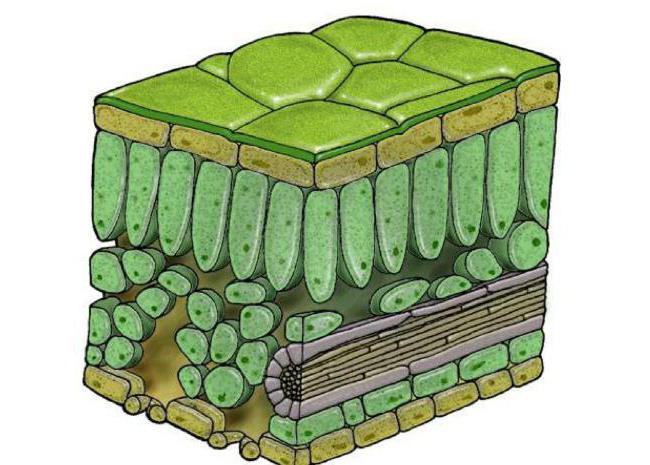
The undersurface is also composed of these transparent cells, closely adjacent to each other. However, among them there are small paired green cells, between which there is a gap. It is this part that is called the stoma. Opening and connecting again, green cells open and close the entrance to the stomata. During these movements, the evaporation of moisture and the process of gas exchange occur. It is known that from 90 to 300 stomata per 1 mm 2 fall on the surface of one leaf plate.
An interesting fact: green cells are almost always located on the side of the leaf on which the maximum air exchange occurs. So, for example, in plants floating on water, capsules or water lilies, the stomata are on the outside, facing the air.
![]()
Varieties
Scientists distinguish two main types of leaves: this leaf is simple and complex. The structure of each of them has its own characteristics. Depending on the appearance, the number of plates and the shape of their edges, compound leaves can also be divided into several types. So, here are the most common types, if selected by external signs:
- fan-shaped (the shape resembles a semicircle);
- spear-shaped (sharp, sometimes there are spines on the surface);
- lanceolate (rather wide, with narrowed edges);
- oval (ovoid shape, which is slightly pointed closer to the base);
- palmate and lobed (they can sometimes be confused, since they both have several lobes);
- palmate (plates diverge from the petiole, the appearance resembles fingers);
- needle (thin and rather sharp).
This list can be continued for a long time, however, the complex shape of the leaf has several more types, depending on the shape of the edges, as well as the location of the leaf blades themselves.

Types of compound plants
Along the edges of the plates, it is very often possible to determine which species a particular plant belongs to. The following forms occur most frequently in nature:
- whole-edge - have smooth edges, on which there are no teeth;
- serrated - as the name implies, such leaves have teeth along the edges;
- fine-toothed - these resemble a saw, which has very sharp and small incisors;
- wavy - these have wavy cutouts that do not have a strict order or standard shape.
Features of each type
It is worth talking more about the distinguishing features of simple and compound leaves, as this can help determine what kind of plant it is and what species it belongs to. So, one of the most noticeable features of each species is the number of plates. If three elements are present, then we have triple-shaped sheets. If five are palmate, and if more, then they are called pinnately divided. On each plate, one can observe a special venation system, due to which nutrients enter the internal tissues. In simple and complex varieties, they differ in shape and structure. Here are the most common types of vein arrangement:
- arcuate (when the venation resembles a menorah in shape - one of the symbols of Judaism);
- transverse;
- longitudinal;
- palmate;
- parallel;
- mesh;
- pinnate.
Another distinguishing feature is the way the leaves are arranged on the stem. Simple and complex - all, without exception, are attached to plant stems in two ways:
- with the help of a cutting, in which case the plant belongs to petioles;
- without a cutting, when the base grows and covers the stem, then we have a sessile plant in front of us.

Leaves of plants: simple and complex
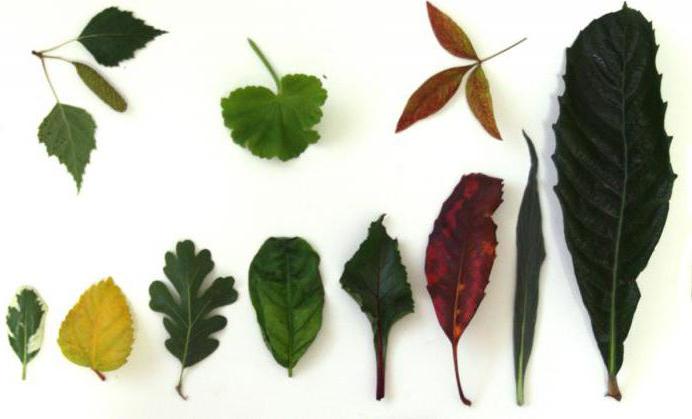
If we classify plants according to the characteristics of leaves, then the following facts can be noted. Simples are commonly found in all herbaceous plants, including shrubs and trees. Complex ones are found both in shrubs and in trees, however, unlike simple ones, during leaf fall they do not fall off all at once, but in parts: first the plates themselves, and then the stalk.
Let's look at examples of the name of simple and complex leaves in plants. Most trees growing in Russia have simple leaves. Aspen, birch and poplar have different shapes: lanceolate, rounded with jagged edges and spear-shaped, respectively. With the onset of autumn colds, the leaves of each of them crumble entirely. They are also found in such fruit trees as apple, pear and cherry; agricultural crops such as oats and corn also have simple leaves.
Complex forms are present on leguminous plants, such as pinnately compound leaves on peas. The following trees have palmate leaves: maple, chestnut, lupine, etc. Remember red clover, its shape is called ternary with ciliated edges.
What are the functions of leaves?
Simple and complex forms of these organs are largely due to climatic conditions. In hot countries, trees have large leaves that serve as a kind of protective fence from the sun's rays.

However, the main irreplaceable function is participation in photosynthesis. As you know, it is thanks to this process that trees can convert carbon dioxide into oxygen by absorbing solar energy.
The second most important process is cellular respiration. With the help of mitochondria, the leaves take in oxygen, and carbon dioxide is exhaled through the stomata, which is then used during photosynthesis. Since photosynthesis occurs only in the presence of light, at night carbon dioxide is stored in the form of organic acids.
Transpiration is the evaporation of water from the leaf surface. This regulates the overall temperature and humidity of the plant. The intensity of evaporation depends on the size and thickness of the plates and on the wind speed at a certain point in time.

Adaptation and modifications
Many leaves - simple and complex - have the ability to adapt to environmental conditions. In the process of evolution, they have acquired the ability to change. Here are the most amazing ones:
- the ability to produce wax that lays on the surface and prevents excessive evaporation of water droplets;
- form reservoirs for water during rains, this happens due to the fusion of the edges in such a way that a bag-shaped container is formed (such forms can be found in many tropical vines);
- the ability to change the surface of the plates, cut leaves prevent the effects of strong winds, thereby protecting plants from damage.
Many facts related to the vital activity of these irreplaceable plant organs are still poorly understood. These wonderful decorations of nature itself, in addition to the above functions, perform another aesthetic task - they delight people with their splendor and variety of bright colors!
