Bryophytes are one of the divisions of spore plants, which occupies a special position in the system of this kingdom. Representatives have economic, medicinal value, are widely used and are important participants in food chains. In addition, they take part in the formation of marsh ecosystems.
Sphagnum: systematic position
According to their place in sphagnums, they occupy the following taxonomic position:
- Kingdom: Plants.
- Department: Bryophytes;
- Class, order and family - Sphagnum.
- Genus: Sphagnum.
The number of species reaches 120, of which the most widespread are such as:
- swamp sphagnum;
- protruding;
- brown;
- Magellanic;
- papillose;
- Girgenzon.
The structure of sphagnum has some features, which leaves an imprint on its use by humans. Let's consider this question in more detail.
The external structure of the plant
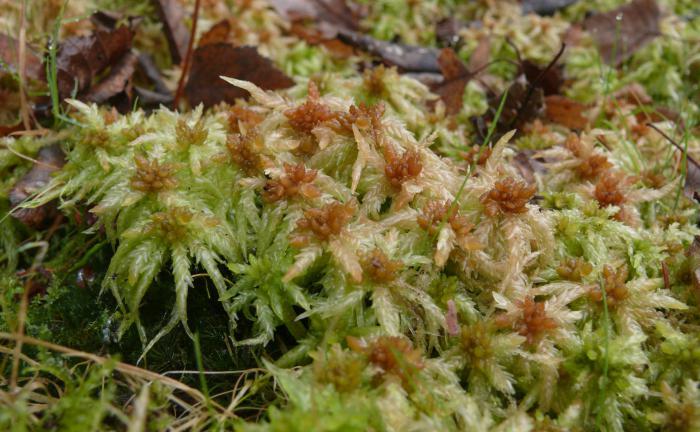
Probably everyone has seen a green loose mat of stems crowded at the top, which forms hummocks of swamps and swamps and floats on the surface of overgrown lakes. so this is sphagnum. A photo of this plant can be seen below.
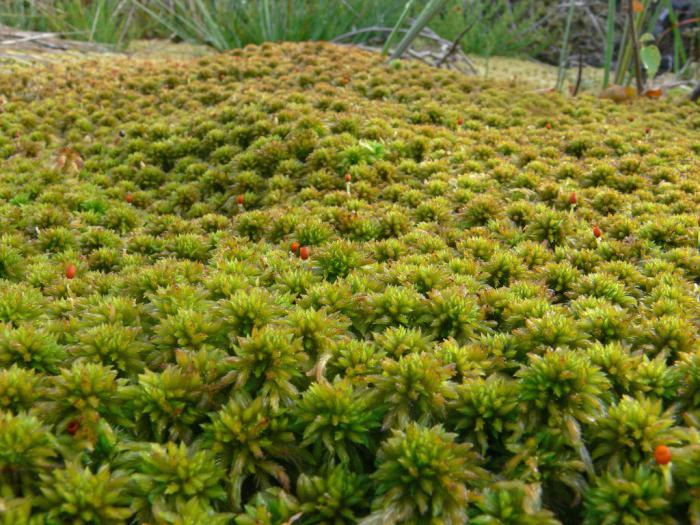

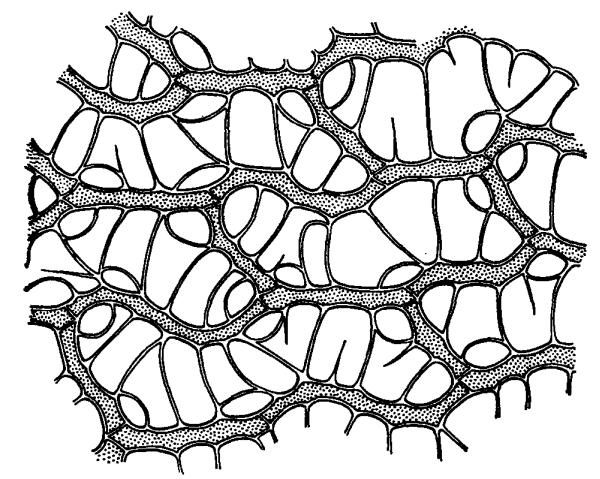
Very nice juicy stems, repeatedly dissected and crowded up. Outside covered with a crust, which is several layers of cells. Sphagnum leaves are sessile, reed type. Those that are located on the stem are oblong and often solitary. And the leaves of the branches, on the contrary, are more crowded, bent at the top. In fact, they are almost scaly and barely visible without special equipment. What is usually mistaken for leaves are the numerous branches from the main stem.
Like other mosses, sphagnum mosses lack roots. However, unlike relatives, they do not have rhizoids for attachment to the substrate. Interestingly, the lower the stem is viewed, the lighter it appears. Finally, at the base it completely loses its green color. This is due to the absence of the chlorophyll pigment in the cells, since these structures are no longer alive, but dead.
From such parts, settling to the bottom of the swamp, peat is subsequently formed. That is why sphagnum is often In general, the color of the plant is pale green, not bright. This is due to the fact that it is constantly saturated with a large amount of water. The question arises: "How does moss manage to store so much liquid in itself?" This is due to the peculiarities of the internal structure. Let's consider them.
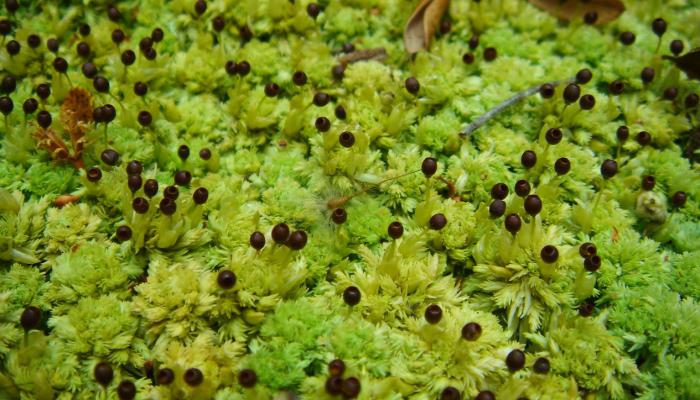

The internal structure of sphagnum
From the inside, moss is formed by ordinary cells. Sphagnum leaves contain chlorophyll, as do stem structures. Therefore, photosynthesis is carried out by almost the entire surface of the body. The same happens with nutrition, that is, the absorption of water.
Green moss cells are connected to each other by the ends and form a structure resembling a network - this is the conducting system of the plant. The reproductive organs are sporangia, in which spores mature.
There is no conducting system of this kind. Instead, there are special cells. It is they who perform the functions of storing and absorbing water.
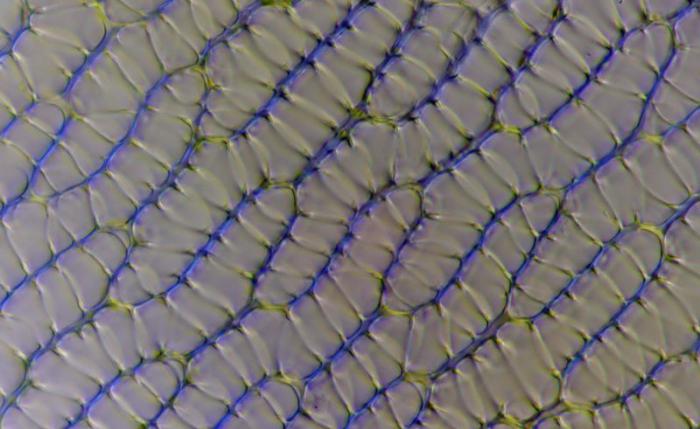

Special cells in the structure
Sphagnum cells are not all the same. The fact is that some of them have shells with a hole and a dead protoplast, that is, an empty cavity. This is necessary for the plant in order to absorb a large amount of moisture and keep it inside itself in these hollow structures.
The structure of sphagnum allows it to fill with water in an amount 20-30 times its own weight. That is why in the habitats of these mosses it is always very humid, they literally float on the surface of the water.
When the plant is filled with moisture, its color is soft green. During a drought, it gradually turns white, eventually becoming completely snow-white.
Moss reproduction
The structure of sphagnum includes specialized structures necessary for reproduction - sporangia. They, like all other mosses, are located on special stems in the apical part of the plant. They are a box with a lid in which the formation and maturation of spores takes place.
When the time comes for reproduction, small cells spill out and are carried by the wind. Once in a drop of water, they begin to germinate into a new plant. The lid of the sporangium opens spontaneously.
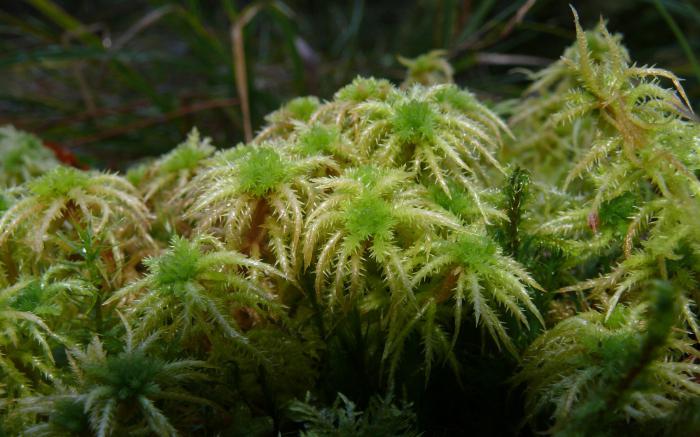

There is another way of reproduction that this plant carries out. Sphagnum is able to give vegetative parts for further independent existence. Most often this happens after the main stalk grows strongly in length, towering above the rest of the parts. At this point, the separation of the daughter plant occurs.
Special properties of sphagnum mosses
The photo of which can be seen in this article has a number of special properties due to the presence of special cells. This:
- Hygroscopicity exceeding all known limits in plants. If we compare the ability to absorb moisture of cotton wool and sphagnum, then in moss it will be 6 times more! In addition, it is noteworthy that the distribution of water inside the body of the plant occurs absolutely evenly. Therefore, until all the existing cells are filled, the moss will not give up excess moisture. This allows you to use it as a supplement to the soil.
- Breathability, which allows the soil with moss to be very light, loose and airy. This increased aeration has a positive effect on the growth and development of other plants in the ecosystem.
- Sphagnum acids, which are part of the plant, allow it to moderately acidify the soil with hydrogen cations.
- The rich material organic composition makes this plant special. Sphagnum has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as disinfectants.
What is the composition of these amazing mosses? You can name the most important connections:
- sphagnum acids;
- coumarins;
- sphagnol;
- terpenes;
- carbolic acid.
Due to this component composition, the plant itself is practically not exposed to either diseases or pests.
Places of growth
The main condition for the growth of this plant is the presence of a sufficient amount of moisture. After all, sphagnum moss, the photo of which is in the review, is very dependent on water during reproduction, like all spores. That is why it can be attributed to the main places of growth:
- temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere;
- european part of Russia;
- Siberia;
- South America.
The main ecosystem that this moss forms is raised bogs. Wherever such a plant settles, there is a gradual and inevitable swamping of the area.

Role in nature
The whole life of sphagnum is built on its ability to absorb moisture. Features of the internal and external structure, economic importance and scope, use for medical purposes - almost everything is explained by the composition and structure. The role performed in nature also owes this.
The main thing is that the sphagnum, the photo of which we posted in the article, forms peat deposits. Due to the sphagnic acid and sphagnol that are part of the plant, the processes of decay and decomposition of the dead lower parts of the plant are extremely slow. This leads to the formation of peat layers. The action takes place slowly, about one meter per thousand years.
It is also important the property to cause swamping of the area. As a result, not only the vegetation cover changes, but the entire biogeocenosis, fauna, insects and other creatures in general.

Economic importance for humans
There are several main areas of application of this moss by humans.
Thus, it turns out that sphagnum peat moss is not only an interesting and valuable plant as a source of minerals, but also an invaluable storehouse of medicines, a source of moisture and an aerator for other representatives of the flora. Its beautiful appearance is harmoniously combined with the spectacular characteristics of the internal structure and significance in nature and people's lives.
