Escape modifications
Above-ground modifications of shoots:
1. Kidney - a shortened modified shoot with rudimentary leaves, nodes, internodes.
2. Flower - a shortened modified shoot, the leaves of which have turned into parts of a flower.
3. Spines - modified lateral (hawthorn) or apical shoots (camel thorn).
4. Head of cabbage (cabbage) - a metamorphosed giant bud surrounded by succulent leaves.
5. Phyllocladia - flattened green axillary shoots similar in appearance to a leaf. However, they bear flowers, fruits, and scaly leaves (butcher's needle).
6. Fleshy stems of stem succulents (cacti) that store water.
7. Antennae - in cucumber and grapes.
Rice. 28. Above-ground modifications of the stem:
a - phyllocladia (needle needle), b - thorn, c - fleshy stalk of succulent (opuntia), d - antennae (grapes).
Underground escape modifications:
1. Rhizomes are underground modified shoots that are similar in appearance and functions to roots, but, unlike roots, do not have a root cap, they carry grassroots leaves, axillary and apical buds, leaf-like scars, adventitious roots. Adapted for vegetative propagation, transfer of adverse conditions, supply of nutrients. In the direction of growth, the rhizomes are: horizontal (iris) (Fig. 29), vertical (hellenic), oblique (lily of the valley). 
Rice. 29. Rhizome of iris (iris). Rice. 30. Potato tuber.
2. A tuber is an elevated or underground modified shoot, which is a thickened stem, bears scales (lower leaves), leaf scars, buds - eyes. Characteristic for potatoes, Jerusalem artichoke, etc. (Fig. 30).
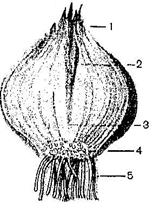
3. The bulb is a shortened stem (bottom), bearing numerous leaves closely converging (dry and juicy scales); at the top of the donets is a kidney. Dry scales perform a protective function, and juicy scales store water and nutrients. They are found in onions, garlic, galanthus, ungernia. (Fig. 31).

Rice. 31. Fig. 32.
Rice. 31. Onion bulb.
1 - dry scales, 2 - juicy scales, 3 - kidney, 4 - bottom, 5 - adventitious roots.
Rice. 32. Corm in section.
1 - apical bud, 2 - bottom, 3 - adventitious roots.
4. Corm - outwardly similar to an onion, but morphologically closer to a tuber: all its leaf scales are dry, and reserve substances are deposited in the stem part (crocus, gladiolus).
leaf morphology
The leaf is a lateral vegetative organ that has limited growth and grows at the base. Adapted for photosynthesis and transpiration (evaporation of water) and gas exchange. Sometimes reserve nutrients, water (aloe) are deposited in the leaves.
The sheet is divided into the following parts:
1. leaf blade - performs the main functions of the leaf: photosynthesis and transpiration.
2. The petiole attaches the leaf to the stem, orients the lamina with respect to light, conducts water and organic matter into and out of the leaf. If the petiole does not develop, then the leaf is called sedentary.
3. Leaf sheath - this is a strongly overgrown base of a leaf or petiole, covering the node entirely (cereals) or partially (celery).
4. Stipules - paired formations at the base of the petiole, play a protective role.
5. Bell - stipules fuse with each other, covering the stem of the plant (Fig. 33).
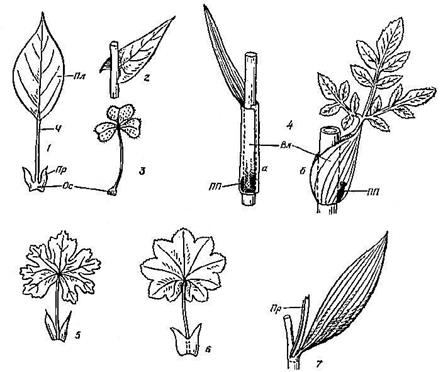
Rice. 33. Parts of the sheet:
1 - petiolate, 2 - sessile, 3 - with a pad at the base, 4 (a, b) - with a sheath, 5 - with free stipules, 6 - with adherent stipules, 7 - with axillary stipules. Pl - plate, Os - base, Vl - vagina, Pr - stipule, H - petiole, PP - axillary kidney.
In the leaf blade, the base and top of the leaf are distinguished (Fig. 34, 35).
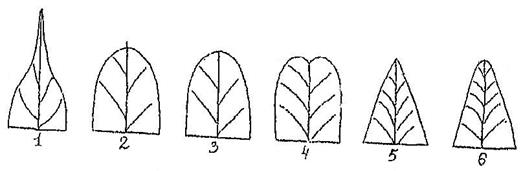
Rice. 34. The tip of the leaf blade.
1. Elongated pointed (with a narrow long sharp end).
2. Pointed (with a thin and short spine).
3. Rounded (in the form of a correctly convex arc).
4. Notched (in the form of a notch).
5. Sharp (in the form of an acute angle).
6. Dull (in the form of a cut corner).
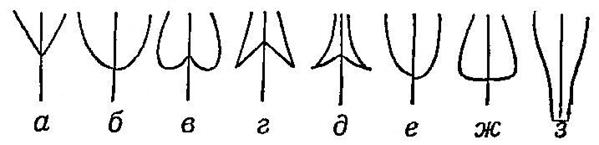
Rice. 35. Leaf base: a - wedge-shaped, b - rounded, c - heart-shaped, d - arrow-shaped, e - spear-shaped, f - unequal-sided, g - truncated, h - descending.
Leaf venation is a system of conducting bundles in leaf blades through which substances are transported. In dicotyledonous plants, two main types of venation are known - pinnate and palmate nerve.
Leaves with peritoneural venation have one main vein, which is a continuation of the petiole. Lateral veins of the first order depart from it, veins of the second order depart from them, etc. (Fig. 36).
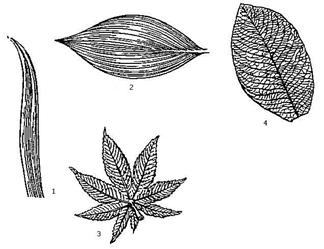
Rice. 36. Types of leaf venation.
