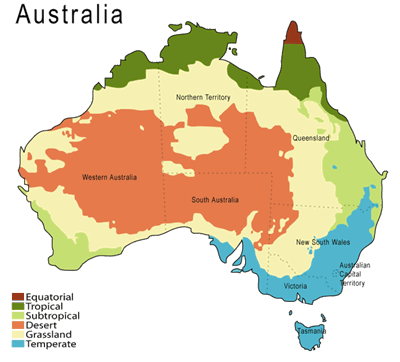
Australia Three climatic zones cross: subequatorial, tropical and sub-tropical (Fig. 95). The northern part of the mainland is located in subequatorial climatic zone. Here, throughout the year, constantly high temperatures prevail (about +25 ° C) and a large amount of precipitation falls (about 1500 mm). Seasonal differences regarding precipitation are clearly observed - very humid summers and dry winters with thunderstorms and showers.
AT tropical climate zone against the background of high air temperatures (in summer, in January, +30 ° С, in winter, in July, +16 ° С) two types of climate are distinguished - continental (deserted) and wettropical. They differ mainly in the nature of moisture. In areas with a tropical desert type of climate, about 200 mm of precipitation falls annually. In areas of tropical humid climate in the east of the continent, the amount of precipitation can be 10 times greater. The amplitude of temperature fluctuations, on the contrary, is much larger in the interior of the mainland. Material from the site
Subtropical climate zone covers the southern part of the mainland. The air temperature in this zone is positive throughout the year, but the amount and mode of precipitation vary significantly from west to east. Southwest Australia climate mediterranean, with dry summers and wet winters. The central part of the belt is inherent continental subtropical A type of climate with dry, hot summers and relatively cold winters. Southeast dominates humid subtropical type of climate with even precipitation throughout the year.
AT temperate climate zone Only the island of Tasmania is located. Under the influence of the prevailing moderate air mass, winters here are relatively warm with unstable weather, strong westerly winds and a mild summer. Over 1000 mm of precipitation falls annually on the island.
Australia It is located in three climatic zones: subequatorial, tropical and subtropical.
On this page, material on the topics:
Lectures on the geography of continents and oceans
Report on the tropics climate zone 3 sheets
Australia climate table
Australia belt table
Type of climate Australia
Questions about this material:
Australia is a continent that was not immediately studied by Europeans, far and unusual. In addition, it is completely located in the other hemisphere, and is also the smallest on Earth. To study its features will be interesting to everyone who wants to have an idea of \u200b\u200bthe climate and nature of different corners of the earth.
Mainland geography
Australia comes from Latin australis, which means "southern". Thus, the name of the mainland is directly related to its location. The extreme northern point of the continent is Cape York. In the south is South East Point. In the west, Australia ends at Cape Point and in the east, Byron. The continent is 3,200 kilometers from north to south. From west to east, it occupies 4,100 km. Only at the beginning of the nineteenth century did Australia appear on the maps. General information about the continent became available as a result of numerous pioneering trips. The English captain Matthew Flinders rounded him completely and gave the name. The geography of the mainland includes several climatic zones and each should be considered in detail. Around the continent are groups of islands - Melville, Bathurst, Tasmania, Groot Island, Derk Hartog, Flinders, Fraser and Kangaroo.

The waters around the mainland
The presence of oceans directly affects the climate Australia has. Rivers and lakes also play a role. The mainland has no connection with other continents; it is washed by the Pacific and Indian oceans. In the north are the seas - Arafur and Timor. The largest bay is the Carpentarium. Shallow water stretches along the southern and western coasts without pronounced currents. From the east, Australia is washed by the Coral and Tasman Seas, the relief of which includes deep basins. Gutters are located along the island arcs. Their depth can reach ten kilometers. 
We continue our conversation about such a continent as Australia. Climate, climatic zones and regions of this continent we will consider further.
Subequatorial climate
A strip of this type of weather spans north and northeast. Answering the question, in which zones is mainland Australia located, the subequatorial climate is worth mentioning first, along with tropical and subtropical. This region is distinguished by a small amplitude of annual temperatures and impressive precipitation volumes, sometimes reaching more than 2000 millimeters. They bring to earth means that everything happens in the summer. In the winter season, the air becomes dry, hot winds blow from the continent, sometimes they can lead to drought. 
Tropical climate
When answering the question in which climatic zones Australia is located, do not forget about this strip. Especially on the mainland, it is expressed in two versions. A humid tropical climate distinguishes the extreme eastern part, falling under the action of the southeast trade wind. The trade winds carry the air masses of the Pacific Ocean, full of moisture, perfectly moisturizing the earth. On average, up to 1,500 millimeters of precipitation falls here. The warmest month has a temperature of twenty-five degrees, and the coldest - at thirteen.
When determining which climate zones Australia is located in, one should not forget about the effect of the relief - it is difficult to penetrate the masses of air behind the Great Dividing Range, therefore there is rainfall only on the western slopes and foothills. In the center and in the west - a desert tropical climate with average summer temperatures of thirty degrees and the same winter as in the previous type. What is Australia's desert climate? There is the hottest area. In the area of \u200b\u200bthe city called Alice Springs, the temperature of a summer day can rise to plus forty-five, and at night fall below zero. These territories receive three hundred millimeters of precipitation per year. Sometimes it may not rain for several years. 
Subtropical belt
It is divided into three varieties - Mediterranean, humid and continental. The first distinguishes the southwestern region. He, as the name implies, resembles the conditions of European countries - France and Spain. The Mediterranean climate is characterized by hot and dry summers. Winter is wet and warm. The annual temperature amplitude is quite small: from +23 degrees in January to +12 in June. Precipitation is up to a thousand millimeters. In the continental climate are the state of New South Wales and the surrounding area of \u200b\u200bAdelaide. The main features of this zone are a small amount of precipitation and impressive temperature fluctuations over the year. Finally, a subtropical humid climate is characteristic of the state of Victoria and the southwestern foothills. Mild weather prevails here with a lot of rainfall. In summer, the temperature reaches +24, and in winter it drops by 15 degrees. The local area is great for growing vegetables and fruits, grazing dairy cattle or sheep.
Now you know in what climatic zones the mainland Australia is located, and you can pay attention to other details. 
and semi-desert
In addition to the climate, it is worth considering these natural areas. The climatic zones in which Australia is located also affects these zones. So, one of the common zones are characteristic of the northern part of the mainland. Physical weathering leads to the appearance of a specific relief. This area is distinguished by such deserts as Big Sandy, Simpson, Big Victoria. They are characterized by high temperatures during the day with possible frosts at night. The difference between the Australian deserts and many others is that there is enough moisture for some vegetation. The fauna is poorly represented. Antelopes, marsupial moles, hyenas, jackals are found in the desert and semi-desert zones. A variety of jerboas and gerbils prevail, as well as reptiles. In the fixed sands, more animals live than in the rocky area. 
Equatorial Forest Zone
As mentioned above, in which climatic zones Australia is located, it also affects the natural areas encountered here. The zone is found on the east coast of Australia. To form such a territory, more moisture and precipitation are needed in an amount of more than two thousand millimeters per year. Hot temperatures are above twenty degrees, and such a volume of rain is provided by warm currents. In such an area there are several tiers of plants with an upper one reaching forty meters. Australian eucalyptus can reach even a hundred! Plants of such territories have very large leaves that remain green all year round. A variety of snakes, frogs, spiders, lizards and insects live here. Animals most often differ in small size (for example, koalas). There are also monkeys. Larger animals simply could not move in either the lower or upper levels of such an area, filled with thick branches, large leaves and large tree trunks.
Savannah zone
The climate zones in which the mainland Australia is located allows it to differ in special geographical areas. For example, the sandstones of the savannah, located in the north, are a kind of natural attraction. The rivers flowing from the mountains flood this zone, as a result of which vast floodplains are developed. So there is a wet savannah interspersed with rain forests and small shrubs. Many herbs and shrubs grow here. Knowing in which climatic zones the mainland Australia is located, one can not be surprised at the unique nature. However, the world-famous national park called "Cockatoo" is still impossible to overlook. This is an amazing place with virgin patches of vegetation.
The Australian continent is located within the three main warm climatic zones of the southern hemisphere: subequatorial (in the north), tropical (in the central part), subtropical (in the south). Only a small part of the island of Tasmania is within the temperate zone.
The subequatorial climate, characteristic of the northern and northeastern parts of the Australian continent, is characterized by an even temperature course (during the year the average air temperature is + 23 ° С; + 24 ° С) and a large amount of precipitation (from 1000 to 1500 mm, and in some places more than 2000 mm.). Rainfall is brought here by the moist northwest monsoon, and they fall mainly in the summer. In winter, in the dry season, rains fall only occasionally. At this time, dry, hot winds blow from the interior of the mainland, which sometimes cause droughts.
In the tropical zone on the Australian continent, two main types of climate are formed: tropical wet and tropical dry.
A tropical humid climate is characteristic of the extreme eastern part of Australia, which is part of the southeast trade winds. These winds bring with them to the mainland moisture-saturated air masses from the Pacific Ocean. Therefore, the entire area of \u200b\u200bcoastal plains and eastern slopes of the Great Dividing Range is well moistened (on average, from 1000 to 1500 mm of rainfall) and has a mild warm climate (the temperature of the warmest month in Sydney is + 22 ° C; + 25 ° C, and the coldest - + 11.5 ° С; + 13 ° С). Masses of air that bring moisture from the Pacific Ocean penetrate beyond the Great Dividing Range, losing a significant amount of moisture along the way, therefore precipitation falls only on the western slopes of the ridge and in the foothills.
 Located mainly in tropical and subtropical latitudes, where solar radiation is high, the Australian mainland is very hot. Due to weak ruggedness coastline and the elevation of the marginal parts, the influence of the seas surrounding the mainland is weak in the interior of Australia.
Located mainly in tropical and subtropical latitudes, where solar radiation is high, the Australian mainland is very hot. Due to weak ruggedness coastline and the elevation of the marginal parts, the influence of the seas surrounding the mainland is weak in the interior of Australia.
Australia is the driest continent on Earth, and one of the most characteristic features its nature - widespread deserts, which occupy vast spaces and stretch almost 2.5 thousand km from the shores of the Indian Ocean to the foothills of the Great Dividing Range.
The central and western parts of the continent are characterized by a tropical desert climate. In summer (December-February) average temperatures here rise to + 30 ° С, and sometimes even higher, and in winter (June-August) they decrease on average to + 10 ° С; + 15 ° C. The hottest region of Australia is the northwestern region, where in the Great Sandy Desert the temperature almost all summer stays at + 35 ° C and even higher. In winter, it decreases slightly (approximately to + 25 ° C; + 20 ° C). In the center of the mainland, near the city of Alice Springs, in the summer, the temperature rises during the day to + 45 ° С, at night drops to zero and lower (-4 ° С; -6 ° С).
The central and western parts of Australia, that is, about half of its territory, receive an average of 250-300 mm of rainfall per year, and the vicinity of Lake Eyre - less than 200 mm; but even these minor precipitation falls unevenly. Sometimes for several years in a row there is no rain at all, and sometimes in two or three days, or even in a few hours, the entire annual amount of rain falls. Part of the water quickly and deeply seeps through the permeable soil and becomes inaccessible to plants, and part evaporates under the hot rays of the sun, and the surface layers of the soil remain almost dry.
Within subtropical zone Australia has three types of climate: Mediterranean, subtropical continental and subtropical humid.
The Mediterranean climate is characteristic of southwestern Australia. As the name suggests, the climate of this part of the country is similar to the climate of European Mediterranean countries - Spain and southern France. Summer is hot and usually dry, and winter is warm and humid. Relatively small temperature fluctuations over the seasons (January - + 23 ° C; + 27 ° C, June - + 12 ° C; + 14 ° C), a sufficient amount of precipitation (from 600 to 1000 mm).
The subtropical continental climate zone covers the southern part of the mainland adjacent to the Great Australian Gulf, includes the surroundings of the city of Adelaide and extends somewhat further east, to the western regions of New South Wales. The main features of this climate are a small amount of precipitation and relatively large annual temperature fluctuations.
The subtropical humid climate zone includes all of Victoria and the southwestern foothills of New South Wales. In general, this entire zone is characterized by a mild climate and a significant amount of precipitation (from 500 to 600 mm), mainly in the coastal parts (the penetration of precipitation into the interior of the continent decreases). In summer, temperatures rise on average to + 20 ° C; + 24 ° С, but in winter they drop quite strongly - up to + 8 ° С; + 10 ° C. The climate of this part of Australia is favorable for growing fruit trees, various vegetables and forage grasses. True, to obtain high yields, artificial irrigation is used, since in summer the soil does not contain enough moisture. In these areas, dairy cattle (grazing on forage grasses) and sheep are bred.
The temperate zone includes only the central and southern parts of the island of Tasmania. This island is largely affected by the surrounding water, and its climate is characterized by moderately warm winters and cool summers. The average January temperature here is + 14 ° C; + 17 ° С, in June - + 8 ° С. The prevailing wind direction is west. The average annual rainfall in the western part of the island is 2500 mm, and the number of rainy days is 259. In the eastern part, the climate is somewhat less humid.
In winter, snow sometimes falls, but it does not persist for a long time. Heavy rainfall favors the development of vegetation, and especially grasses that vegetate year-round. Herd of cattle and sheep graze year-round on evergreen succulent natural and improved sowing of forage grasses, meadows.
The hot climate and insignificant and uneven precipitation in most of the continent lead to the fact that almost 60% of its territory lacks runoff to the ocean and have only a rare network of temporary streams. Perhaps no other mainland has such a poorly developed inland water network as in Australia. The annual runoff of all rivers of the Australian continent is only 350 km³.
In three latitudes: subequatorial, subtropical and tropical. The northern part of Australia is the subequatorial belt, the southern part is the subtropics, and most of the continent is the tropics.
The climate of Australia in the northern part is characterized by a large amount of rainfall, about two thousand millimeters. Most of them are brought from the northwest by the wet monsoon in the summer. In winter, the amount of precipitation decreases significantly, at this time there is more likely a drought, which is brought by hot winds. The average annual temperature fluctuations are small.
The tropical latitudes of the continent - it is here that the two main dry and humid tropical are formed. The extreme eastern region is under the influence of a humid tropical climate, moisture comes here with the air masses of the Pacific expanses. The eastern slope of the Great Dividing Range and coastal plains receive annual precipitation in an amount from a thousand to one and a half thousand millimeters. The climate of Australia in this part is characterized by a warm, soft and fairly even "temper": the temperature of the warmest days is about twenty-five degrees, and the coldest - ten. Located in the tropics and subtropics, the mainland heats up significantly. This means that the climate in Australia is arid and hot.
Almost the entire central part of the mainland is desert. They occupy huge spaces with a length of about two and a half kilometers. The climate of Australia - desert tropical - prevails in the west and in the central part. In summer, the temperature here exceeds thirty degrees, and in winter does not drop below ten degrees. The large sandy desert is the hottest area on the continent. Here the difference between the temperatures of summer and winter is only ten to fifteen degrees. And the climate of Australia in this region is characterized by a scanty amount of precipitation.
The part of the mainland, located in the subtropics, is climatically divided into three zones: Mediterranean, subtropical continental and subtropical wet.
The first zone is close to the mild climate of the Mediterranean countries. It is hot and sometimes dry in summer, and wet and warm in winter. As for precipitation, it is enough here - from six hundred to a thousand millimeters per year.
The subtropics should include the southern part of the continent, where it extends up to the western part of New South Wales. Here, temperature rises significantly during the year, and precipitation does not differ in special abundance.
Victoria, the southwestern foothill of New South Wales, has its own climatic features. This part of Australia has a mild, warm and humid climate, and the amount of precipitation in the coastal areas ranges from five hundred to six hundred millimeters per year. Going deeper to the center of the mainland, precipitation is becoming less and less. This part of Australia is favorable to agriculture, although there is a need for additional artificial irrigation. At the same time, rivers and lakes in most of the continent do not have direct drains into the ocean, because the waters of most lakes are salty, and rivers during the hot months have the peculiarity of partially drying out. In summer, the air temperature reaches twenty-five degrees, and in winter does not drop below ten.
Of particular interest is winter in Australia. If the summer period is relatively even, then the winter in different climatic regions is completely different. So, for example, the interior of the mainland is characterized by hot and dry winters, since those coming from the ocean, on their way to the center of the continent, have time to warm up and lose most of their moisture. In the capital, winter is characterized by low temperatures and the presence of snow.
Australia is the only country in the world covering an entire continent. True, this is the smallest continent on Earth: its area is 7,686,850 square kilometers, which is about half the size of Russia. Nevertheless, in the Australian territory it can fit 32 times, for example, Great Britain, and about two times - all of continental Europe (except for the Russian part).
Situated between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, Australia is known as a country with wonderful warm weather and great diversity. climatic conditions.
According to the generally accepted classification of climatologist Vladimir Köppen, there are six climatic zones in Australia - from the hot equatorial in the north of the mainland to the cold alpine in the Victoria Mountains, where the highest point of the continent, Mount Kosciuszko.
But if you do not go into scientific details, the general picture of the climatic conditions of Australia is as follows: the northern and central parts of the continent in the tropical and subequatorial zones, and the southern regions dominated by the subtropics and temperate climate.
Like other countries in the southern hemisphere, the seasons in Australia are the opposite of what we are used to. From December to February there is summer, from March to May - autumn, from June to August - winter months and from September to November - spring.
In most of the north of the Australian continent there are no extreme weather conditions and serious temperature extremes. Cool winters pass with an average temperature of + 13 ° C, and the average temperature in the warm season reaches + 29 ° C.
This happens because the climate characteristic of tropical latitudes brings only two weather seasons - wet and dry.
During the dry season - from May to October - it is almost always sunny, the average humidity is 30%. The wet season lasts in Australia from November to April, this is the time of monsoons, tropical cyclones and thunderstorms.
However, in a number of regions the climate may be sharper, with a significant difference in temperature. This applies primarily to the sparsely populated central Australia, where the desert climate dominates, suggesting a sharp change in temperature during the day. Measurements in Alice Springs located here show rise to + 40 ... 45 ° C during the day and sometimes drops to 0 ° C at night. Central Australia is considered unsuitable for living, but there are national parks and extractive industries. So going to Australia, biologists and geologists should be prepared for such weather.
In the southern parts of the country, the most fertile soils are located and most of the population lives. In the south-east of Australia there are also its capital Canberra and the two largest cities - Sydney and Melbourne.
These regions are characterized by a temperate climate. Unlike the north of Australia, it is noticeably cooler here, you can distinguish all four seasons, and the number of sundials reaches an impressive figure of 3000 per year! For comparison, the sunniest city in Russia - the resort of Anapa - receives only 2400 hours of cloudless sky annually, and Moscow is almost one and a half times less.
Meteorological phenomena
The average annual rainfall in Australia is approximately the same for all seasons and barely exceeds 400 mm (in Moscow - 705 mm). However, in the southern agricultural zone, more prevailing are wet westerly winds, which can bring up to 700 mm of precipitation per year.
Due to the nature of the Australian climate, travelers from other countries are best able to plan a trip to northern Australia between June and September, before the hot season begins. It is best to visit southern Australia between November and March, when warm and sunny days begin there.
Other times are suitable for those who are interested in sudden vagaries of the weather. For example, in September (i.e., the beginning of spring) of 2009 in Sydney, airports were closed for a whole day due to a severe dust storm, roads were blocked, and most of the city was covered with a layer of tiny reddish dust brought by the wind.
It is in Australia that one of the most amazing meteorological phenomena in the world can be observed - clouds with the name Morning Gloria. This rare and majestic sight arises from the end of September until the beginning of November in the north of the country, in the Gulf of Carpentaria, and is a series of moving cylindrical clouds reaching thousands of kilometers in length and two kilometers in diameter.
The appearance of “Morning Gloria” is always accompanied by a squalling increase in wind and sharp surges in pressure on the surface, while the clouds themselves, moving at a speed of up to 60 kilometers per hour, do not change their elongated shape.
The weather of the continent can bring both pleasant and unpleasant surprises, but in general, coastal Australia, especially its southern part, has a warm sunny climate, almost ideal for a comfortable life, efficient work, and for
