The primitive era of mankind is the period that lasted before the invention of writing. In the 19th century it received a slightly different name - “prehistoric”. If you do not delve into the meaning of this term, then it unites the entire time period, starting from the origin of the Universe. But in a narrower perception, we are talking only about the past of the human species, which lasted until a certain period (it was mentioned above). If the funds mass media When scientists or other people use the word “prehistoric” in official sources, the period in question must be indicated.
Although the characteristics of the primitive era have been developed by researchers bit by bit for several centuries in a row, discoveries of new facts relating to that time are still being made. Due to the lack of writing, people compare data from archaeological, biological, ethnographic, geographical and other sciences for this purpose.
Development of the primitive era
Throughout the development of mankind, various options for classifying prehistoric time have been constantly proposed. Historians Ferguson and Morgan divided it into several stages: savagery, barbarism and civilization. The primitive era of humanity, which includes the first two components, is divided into three more periods:
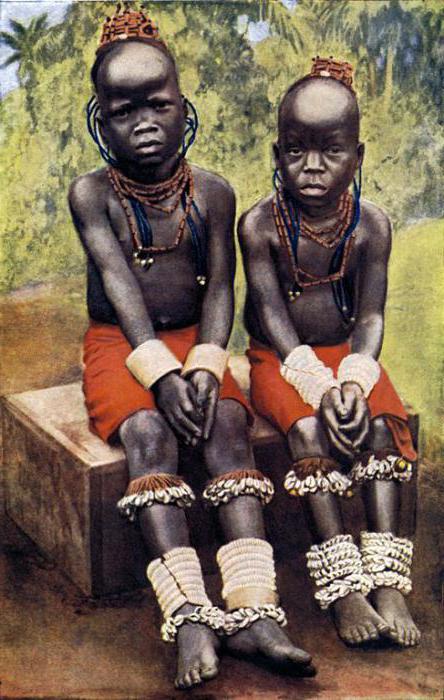

Stone Age
The primitive era received its periodization. We can highlight the main stages, among which was and At this time, all weapons and items for Everyday life made, as you might guess, from stone. Sometimes people used wood and bones in their works. Towards the end of this period, clay dishes appeared. Thanks to the achievements of this century, the area of human settlement on the inhabited territories of the planet has changed greatly, and it was also as a result of it that human evolution began. We are talking about anthropogenesis, i.e. the process of the emergence of intelligent beings on the planet. The end of the Stone Age was marked by the domestication of wild animals and the beginning of the smelting of certain metals.
According to time periods, the primitive era to which this century belongs was divided into stages:

Copper Age
The eras of primitive society, having a chronological sequence, characterize the development and formation of life in different ways. In different territorial regions the period lasted for different times (or did not exist at all). The Eneolithic could have been combined with the Bronze Age, although scientists still distinguish it as a separate period. The approximate time period is 3-4 thousand years BC. It is logical to assume that this primitive era was usually characterized by the use of copper implements. However, the stone never went out of fashion. Acquaintance with new material happened rather slowly. When people found it, they thought it was a stone. The usual treatment at that time - hitting one piece against another - did not give the usual effect, but still the copper was deformable. When cold forging was introduced into everyday life, work with it went better.
Bronze Age
This primitive era became one of the main ones, according to some scientists. People learned to process certain materials (tin, copper), due to which they achieved the appearance of bronze. Thanks to this invention, a collapse began at the end of the century, which occurred quite synchronously. We are talking about the destruction of human associations - civilizations. This entailed a long development of the Iron Age in a certain area and a too long continuation of the Bronze Age. The latter in the eastern part of the planet lasted a record number of decades. It ended with the emergence of Greece and Rome. The century is divided into three periods: early, middle and late. During all these periods, the architecture of that time actively developed. It was she who influenced the formation of religion and the worldview of society. 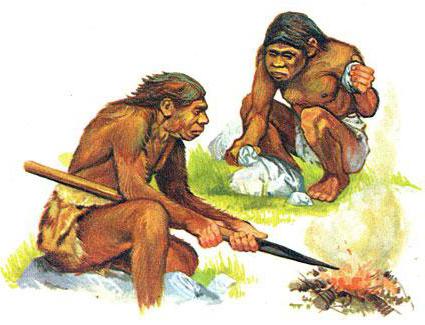
Iron Age
Considering the eras of primitive history, we can come to the conclusion that it was the last one before the advent of intelligent writing. Simply put, this century was conditionally singled out as a separate one, since objects made of iron appeared and were widely used in all spheres of life.
Iron smelting was a fairly labor-intensive process for that century. After all, it was impossible to obtain real material. This is due to the fact that it corrodes easily and does not withstand many climate changes. In order to obtain it from ore, a much higher temperature was required than for bronze. And iron casting was mastered after too long a period of time. 
The emergence of power
Of course, the emergence of power was not long in coming. There have always been leaders in society, even if we are talking about the primitive era. During this period, there were no institutions of power, and there was no political dominance either. Here, social norms were given more importance. They invested in customs, “laws of life,” traditions. Under the primitive system, all requirements were explained in sign language, and violations of them were punished by an outcast from society.
Appeared among different peoples in different time, a multicultural term prehistoric either does not apply, or its meaning and time limits do not coincide with humanity as a whole. In particular, the periodization of pre-Columbian America does not coincide in stages with Eurasia and Africa (see Mesoamerican chronology, chronology of North America, pre-Columbian chronology of Peru). Sources about the prehistoric times of cultures that until recently lacked writing can be oral traditions passed down from generation to generation.
IN foreign literature The term “protohistory” is often used to designate the final stage of the prehistoric era of a culture, when it itself had not yet created its own written language, but is already mentioned in the written monuments of other peoples. This term has not taken root in Russian literature.
Since data about prehistory rarely concerns individuals and does not even always say anything about ethnic groups, the basic social unit of human prehistory is the archaeological culture. All terms and periodizations of this era, such as Neanderthal or Iron Age, are retrospective and largely arbitrary, and their precise definition is a matter of debate.
Primitive communal system- a Marxist term meaning the very first socio-economic formation, when all members of society were in the same relationship to the means of production, and the method of obtaining a share of the social product was the same for everyone (“primitive communism”). From the following stages social development The primitive communal system is distinguished by the absence of private property, classes and the state.
Periods of development of primitive society
At different times, different periodizations of the development of human society have been proposed. Thus, A. Ferguson and then Morgan used a periodization of history that included three stages: savagery, barbarism and civilization, and the first two stages were divided by Morgan into three stages (lower, middle and higher) each. At the stage of savagery, human activity was dominated by hunting, fishing and gathering, there was no private property, and equality existed. At the stage of barbarism, agriculture and cattle breeding appear, private property and social hierarchy arise. The third stage - civilization - is associated with the emergence of the state, class society, cities, writing, etc.
Morgan considered the lowest stage of savagery to be the earliest stage in the development of human society; the middle stage of savagery, according to his classification, begins with the use of fire and the introduction of fish food, and the highest stage of savagery begins with the invention of the bow. The lowest stage of barbarism, according to his classification, begins with the advent of pottery, the middle stage of barbarism with the transition to agriculture and cattle breeding, and the highest stage of barbarism with the beginning of the use of iron.
The most developed periodization is archaeological, which is based on a comparison of man-made tools, their materials, forms of dwellings, burials, etc. According to this principle, the history of mankind is mainly divided into the Stone Age, Bronze Age and Iron Age.
In the 40s of the XX century. Soviet scientists P. P. Efimenko, M. O. Kosven, A. I. Pershits and others proposed systems for the periodization of primitive society, the criterion of which was the evolution of forms of ownership, the degree of division of labor, family relationships, etc. In a generalized form, this periodization can be represented as follows:
2) the era of the tribal system;
3) the era of the decomposition of the communal-tribal system (the emergence of cattle breeding, plow farming and metal processing, the emergence of elements of exploitation and private property).
All periodization systems are imperfect in their own way. There are many examples when stone tools of Paleolithic or Mesolithic form were used by the peoples of the Far East in the 16th-17th centuries, while they had a tribal society and developed forms of religion and family. It is currently believed that the universal periodization of the primitive system ends with the Mesolithic, when cultural development accelerated sharply and proceeded at different rates among different peoples. Below is the currently generally accepted archaeological periodization of the main stages of the development of primitive society. At the same time, cultures that existed simultaneously may be at different stages of development, and therefore, for example, Neolithic cultures may be adjacent to Chalcolithic or to cultures Bronze Age.
| era | Period in Europe | Periodization | Characteristic | Human species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old Stone Age or Paleolithic | 2.4 million - 10000 BC e. |
| The time of hunters and gatherers. The beginning of flint tools, which gradually became more complex and specialized. | Hominids, species: Homo habilis, Homo erectus, Homo sapiens präsapiens, Homo heidelbergensis, Middle Paleolithic Homo neanderthalensis and Homo sapiens sapiens. |
| Middle Stone Age or Mesolithic | 10000 - 5000 BC e. | Begins at the end of the Pleistocene in Europe. Hunters and gatherers developed a highly developed culture of making tools from stone and bone, as well as long-range weapons such as arrows and bows. | Homo sapiens sapiens | |
| New Stone Age or Neolithic | 10000 - 2000 BC e. |
| The emergence of the Neolithic is associated with the Neolithic revolution. At the same time on Far East the oldest finds of pottery appear to be around 12,000 years old, although the European Neolithic period begins in the Middle East with the Pre-Pottery Neolithic. New methods of farming are emerging, instead of gathering and hunting farming (“appropriating”) - “producing” (farming, cattle breeding), which later spread to Europe. The Late Neolithic often progresses into the next stage, the Copper Age, Chalcolithic or Chalcolithic, without a break in cultural continuity. The latter is characterized by the second production revolution, the most important feature of which is the appearance of metal tools. | Homo sapiens sapiens |
| Bronze Age | 3500 - 800 BC e. | Early history | The spread of metallurgy makes it possible to obtain and process metals: (gold, copper, bronze). The first written sources in Western Asia and the Aegean. | Homo sapiens sapiens |
| Iron Age | juice. 800 BC e. |
| Homo sapiens sapiens |
Stone Age
Stone Age - ancient period in the history of mankind, when the main tools and weapons were made mainly of stone, but wood and bone were also used. At the end of the Stone Age, the use of clay spread (dishes, brick buildings, sculpture).
Periodization of the Stone Age:
- Paleolithic:
- Lower Paleolithic - the period of the appearance of the most ancient species of people and widespread Homo erectus .
- Middle Paleolithic - the period of displacement of erecti by evolutionarily more advanced species of people, including modern man. Neanderthals dominated Europe throughout the Middle Paleolithic.
- Upper Paleolithic - period of dominance modern look people throughout the globe during the last glaciation.
- Mesolithic and Epipaleolithic; the terminology depends on the extent to which the region has been affected by the loss of megafauna as a result of glacier melting. The period is characterized by the development of technology for the production of stone tools and general human culture. There is no ceramics.
- Neolithic - the era of the emergence of agriculture. Tools and weapons are still made of stone, but their production is being brought to perfection, and ceramics are widely distributed.
Copper Age
Copper Age, Copper-Stone Age, Chalcolithic (Greek. χαλκός "copper" + Greek λίθος “stone”) or Chalcolithic (lat. aeneus“copper” + Greek λίθος "stone")) - a period in the history of primitive society, a transitional period from the Stone Age to the Bronze Age. Approximately covers the period 4-3 thousand BC. e., but in some territories it exists longer, and in some it is absent altogether. Most often, the Chalcolithic is included in the Bronze Age, but is sometimes considered a separate period. During the Eneolithic, copper tools were common, but stone ones still predominated.
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period in the history of primitive society, characterized by the leading role of bronze products, which was associated with the improvement of the processing of metals such as copper and tin obtained from ore deposits, and the subsequent production of bronze from them. The Bronze Age is the second, later phase of the Early Metal Age, which replaced the Copper Age and preceded the Iron Age. In general, the chronological framework of the Bronze Age: 35/33 - 13/11 centuries. BC e., but they differ among different cultures. In the Eastern Mediterranean, the end of the Bronze Age is associated with the almost synchronous destruction of all local civilizations at the turn of the 13th-12th centuries. BC e., known as the Bronze Collapse, while in western Europe the transition from the Bronze to the Iron Age dragged on for several more centuries and ended with the emergence of the first cultures of antiquity - ancient Greece and Ancient Rome.
Bronze Age periods:
- Early Bronze Age
- Middle Bronze Age
- Late Bronze Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is a period in the history of primitive society, characterized by the spread of iron metallurgy and the manufacture of iron tools. Bronze Age civilizations go beyond the history of primitive society; other peoples' civilization takes shape during the Iron Age.
History of the development of public relations
The first tools of human labor were a chipped stone and a stick. People earned their livelihood by hunting, which they did together, and gathering. Communities of people were small, they led a nomadic lifestyle, moving around in search of food. But some communities of people who lived in the most favorable conditions then began to move to partial settlement.
The main difference between a tribe of people and an animal pack was the invention of language. Instead of the signal language of animals, which facilitates their coordination during the hunt, people were able to express in language the abstract concepts of “a stone in general”, “an animal in general”. This use of language led to the opportunity to teach young animals with words, and not just by example, to plan actions before the hunt, and not during, etc. The very first tribe of proto-humans to invent language and social organization, based on it, received such gigantic advantages that it quickly displaced all other hominids from their ecological niche, and living humanity is the descendants of this single tribe.
Any spoils were divided among the entire group of people. Tools, household utensils, and jewelry were in the use of individual people, but the owner of the thing was obliged to share it, and in addition, anyone could take someone else’s thing and use it without asking (remnants of this are still found among some peoples).
A person’s natural breadwinner was his mother - at first she fed him with her milk, then generally took upon herself the responsibility of providing him with food and everything necessary for life. This food had to be hunted by men - the mother's brothers who belonged to her clan. Thus, cells began to form, consisting of several brothers, several sisters and the children of the latter. They lived in communal dwellings.
Experts now generally believe that during the Paleolithic and Neolithic times - 50-20 thousand years ago - the social status of women and men was equal, although previously it was believed that matriarchy first reigned.
With the invention of the bow, hunting improved; the dog was tamed and became man's assistant in the hunt.
Gradually, hunting led to the domestication of animals - primitive cattle breeding appeared. Agriculture grew from gathering: seeds of wild plants collected by people and not completely used could sprout near dwellings. It is believed that agriculture first originated in Western Asia. This transition was called the Neolithic revolution (X-III millennium BC). The result of the fact that livelihoods became more secure was a significant increase in the total population: at the turn of the 5th-4th millennia BC. e. About 80 million people already lived on Earth. . Later, people mastered the smelting of metals (first copper, then iron), which made it possible to create more advanced metal tools.
The change in the economy from a purely appropriating to a producing one also led to a change in society. Among the agricultural tribes, the type of settlement became a village in which one community lived, which turned from a tribal community into a neighboring one. Large communal houses became a thing of the past and one patriarchal family now lived in each house. Land ownership was collective - within the collective, individuals or families owned plots of land that could be cultivated, but could not be transferred to others for use. Some communities land were redistributed annually, for others the redistribution occurred once every few years, for others, perhaps, plots were distributed for lifelong land use. Tools, housing, household utensils, clothing, jewelry, and household equipment were privately owned, but vestiges of their communal use have survived to this day.
Population growth among farmers and herders was generally higher than among hunter-gatherers due to the greater productivity of the productive economy. Also, a much larger area was suitable for their habitation. Agrarian communities filled the Earth, just as hunters had filled it before.
Men's unions were an important element of social organization. The male part of the community chose a leader from among men who stood out from the general mass with personal talents, knowledge, wealth and generosity. The result of these processes was the emergence of privileged layers of society - leaders, priests, as well as the most successful in economic activity. Wealth inequality has arisen.
At first, neighboring clans and tribes exchanged what nature gave them: salt, rare stones, etc. Both entire communities and individual people exchanged gifts; This phenomenon is called gift exchange. One of its varieties was “silent exchange”. Then tribes of farmers, cattle breeders and those who conducted agricultural and livestock farming emerged and between tribes with different economic orientations, and subsequently within the tribes, the exchange of products of their labor developed.
Tribes of hunters who did not naturally adopt an agrarian way of life began to “hunt” peasant communities, taking away food and property. This is how a dual system of producing rural communities and the princely squads - former hunters - robbing them developed. The princes - the leaders of the hunters - gradually moved from raiding robbery of peasants to regular regulated exactions. For self-defense and saving the vassal population from the raids of competitors, fortresses, fortresses and cities were built.
The first states arose in Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt and Ancient India in the late and early 3rd millennium BC. e.
Now it is difficult to imagine that there was a time when people did not exist on Earth. Several million years ago, nature was more diverse.
The fauna was full of amazing species, the remains of which were found during excavations. The climate was warm and very humid. Gigantic ferns covered the ground. However, the natural world was constantly changing as weather patterns and climatic conditions. Some plant species disappeared and others appeared. Similar changes occurred in the animal world.
Very, very long ago the ancient apes — Dryopithecus(from Greek drys - wood +pithekos — monkey). Small, about the size of a dog, they lived in trees. Dryopithecus were animals, but they became ancient ancestors modern people. Millennia passed. Animal species appeared and disappeared. Nature seemed to be looking for the most successful forms that were better adapted to existence. The animal developed and flora, that is, evolution continued.
Thus, about 4.5 million years ago, a humanoid creature formed in the natural environment, which modern scientists call Australopithecus(from Latin. australis — southern+ Greek pithekos - monkey). The structure of the skeleton and posture made it possible to stand on the hind limbs for a short time. This ability became necessary when, due to the reduction of forest area, australopithecines were forced to live in the steppes. Walking upright made it possible to look around, notice danger from afar, and track prey during a hunt. In addition, standing on its hind limbs, Australopithecus could hold a stick or stone with its front limbs - the first primitive tool. This made them stronger in fights with predators and helped them survive in the struggle for existence. The habit of upright walking helped to move faster, which is why Australopithecus finally switched to upright walking. But they still remained animals, since their actions were guided not by consciousness, but by animal instincts.
Evolution continued, and about 1.75 million years ago another species of animal appeared, which was called prezinjanthropus(from Latin. prae — before + ancient Arabic zinj - name of East Africa + Greek. anthropos- Human).
The movements of the prezinjanthrope were not yet conscious and dexterous, but he already knew how to use stone fragments or sticks. Science calls such a creature “ a skilled person"(in Latin "Homo habilis"). Such humanoid creatures settled throughout Africa and about one million years ago began to colonize Europe and Asia.
The paths that the first people took to territory modern Ukraine, have not been finally clarified. Researchers believe that they moved from East Africa, where their ancestral home was, through Western Asia and the Balkans to Central Europe through Ukrainian Transcarpathia.
The oldest site in Ukraine is considered to be the one found near the village. Korolevo in Transcarpathia. Archaeologists have found primitive sites on the Des-N (Mizin, Pushkari, Mulatov), the Dnieper (Kruglik, Kirillovka), the Dniester (now not the territory of Moldova), in the Donbass (Androsovka).Material from the site
Scientists did not dare to recognize “Habilis” as a person, since it was not inherent in work, i.e., influencing objects with the help of tools, in which the final result is realized. So, work is conscious actions. It is unique to humans.
). As sources about the prehistoric times of cultures that until recently were deprived of writing, there can be oral traditions passed down from generation to generation.
Since data about prehistory rarely concerns individuals and does not even always say anything about ethnic groups, the basic social unit of human prehistory is the archaeological culture. All terms and periodizations of this era, such as Neanderthal or Iron Age, are retrospective and largely arbitrary, and their precise definition is a matter of debate.
Terminology
A synonym for "prehistoric period" is the term " prehistory", which is used less often in Russian-language literature than similar terms in foreign literature (English. prehistory, German Urgeschichte).
To designate the final stage of the prehistoric era of a culture, when it itself has not yet created its own written language, but is already mentioned in the written monuments of other peoples, the term “protohistory” (English) is often used in foreign literature. protohistory, German Frühgeschichte). To replace the term primitive communal system, characterizing the social structure before the emergence of power, some historians use the terms “savagery”, “anarchy”, “primitive communism”, “pre-civilization period” and others. This term has not taken root in Russian literature.
Non-classical historians deny the very existence of communities and primitive communal system, relationship, identity of power and violence.
From the following stages of social development primitive communal system was distinguished by the absence of private property, classes and the state. Modern studies of primitive society, according to neo-historians who deny the traditional periodization of the development of human society, refute the existence of such a social structure and the existence of communities, communal property under the primitive communal system, and further, as a natural result of the non-existence of the primitive communal system - the non-existence of communal agricultural land ownership right up to the end XVIII century in most countries of the world, including Russia, at least since the Neolithic.
Periods of development of primitive society
At different times, different periodizations of the development of human society have been proposed. Thus, A. Ferguson and then Morgan used a periodization of history that included three stages: savagery, barbarism and civilization, and the first two stages were divided by Morgan into three stages (lower, middle and higher) each. At the stage of savagery, human activity was dominated by hunting, fishing and gathering, there was no private property, and equality existed. At the stage of barbarism, agriculture and cattle breeding appear, private property and social hierarchy arise. The third stage - civilization - is associated with the emergence of the state, class society, cities, writing, etc.
Morgan considered the earliest stage of development of human society to be the lowest stage of savagery, which began with the formation of articulate speech; the middle stage of savagery, according to his classification, begins with the use of fire and the appearance of fish food in the diet, and the highest stage of savagery with the invention of the onion. The lowest stage of barbarism, according to his classification, begins with the advent of pottery, the middle stage of barbarism with the transition to agriculture and cattle breeding, and the highest stage of barbarism with the beginning of the use of iron.
The most developed periodization is archaeological, which is based on a comparison of man-made tools, their materials, forms of dwellings, burials, etc. According to this principle, the history of mankind is mainly divided into the Stone Age, Bronze Age and Iron Age.
| era | Period in Europe | Periodization | Characteristic | Human species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old Stone Age or Paleolithic | 2.4 million - 10000 BC e. |
|
The time of hunters and gatherers. The beginning of flint tools, which gradually became more complex and specialized. | Hominids, species: Homo habilis, Homo erectus, Homo sapiens präsapiens, Homo heidelbergensis, Middle Paleolithic Homo neanderthalensis and Homo sapiens sapiens. |
| Middle Stone Age or Mesolithic | 10,000-5000 BC e. | Begins at the end of the Pleistocene in Europe. Hunters and gatherers developed a highly developed culture of making tools from stone and bone, as well as long-range weapons such as arrows and bows. | Homo sapiens sapiens | |
| New Stone Age or Neolithic | 5000-2000 BC e. |
|
The emergence of the Neolithic is associated with the Neolithic revolution. At the same time, the oldest finds of ceramics dating back about 12,000 years appear in the Far East, although the European Neolithic period begins in the Middle East with the Pre-Pottery Neolithic. New methods of farming are emerging, instead of gathering and hunting farming (“appropriating”) - “producing” (farming, cattle breeding), which later spread to Europe. The Late Neolithic often progresses into the next stage, the Copper Age, Chalcolithic or Chalcolithic, without a break in cultural continuity. The latter is characterized by the second production revolution, the most important feature of which is the appearance of metal tools. | Homo sapiens sapiens |
| Bronze Age | 3500-800 BC e. | Early history | The spread of metallurgy makes it possible to obtain and process metals: (gold, copper, bronze). The first written sources in Western Asia and the Aegean. | Homo sapiens sapiens |
| Iron Age | juice. 800 BC e. |
|
Homo sapiens sapiens |
Stone Age
The Stone Age is the oldest period in human history, when the main tools and weapons were made mainly of stone, but wood and bone were also used. At the end of the Stone Age, the use of clay spread (dishes, brick buildings, sculpture).
Periodization of the Stone Age:
- Paleolithic:
- Lower Paleolithic - the period of the appearance of the most ancient species of people and widespread Homo erectus .
- The Middle Paleolithic is the period when erecti were replaced by evolutionarily more advanced species of people, including modern humans. Neanderthals dominated Europe throughout the Middle Paleolithic.
- The Upper Paleolithic is the period of dominance of the modern species of people throughout the globe during the era of the last glaciation.
- Mesolithic and Epipaleolithic; the terminology depends on the extent to which the region has been affected by the loss of megafauna as a result of glacier melting. The period is characterized by the development of technology for the production of stone tools and general human culture. There is no ceramics.
- Neolithic - the era of the emergence of agriculture. Tools and weapons are still made of stone, but their production is being brought to perfection, and ceramics are widely distributed.
Copper Age
Copper Age, Copper-Stone Age, Chalcolithic (Greek. χαλκός "copper" + Greek λίθος “stone”) or Chalcolithic (lat. aeneus“copper” + Greek λίθος "stone")) - a period in the history of primitive society, a transitional period from the Stone Age to the Bronze Age. Approximately covers the period 4-3 thousand BC. e., but in some territories it exists longer, and in some it is absent altogether. Most often, the Chalcolithic is included in the Bronze Age, but is sometimes considered a separate period. During the Eneolithic, copper tools were common, but stone ones still predominated.
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period in the history of primitive society, characterized by the leading role of bronze products, which was associated with the improvement of the processing of metals such as copper and tin obtained from ore deposits, and the subsequent production of bronze from them. The Bronze Age is the second, later phase of the Early Metal Age, which replaced the Copper Age and preceded the Iron Age. In general, the chronological framework of the Bronze Age: 35/33 - 13/11 centuries. BC e., but they differ among different cultures. In the Eastern Mediterranean, the end of the Bronze Age is associated with the almost synchronous destruction of all local civilizations at the turn of the 13th-12th centuries. BC e., known as the bronze collapse, while in western Europe the transition from the bronze to the iron age dragged on for several more centuries and ended with the emergence of the first cultures of antiquity - ancient Greece and ancient Rome.
Bronze Age periods:
- Early Bronze Age
- Middle Bronze Age
- Late Bronze Age
Iron Age
Iron Age coin hoard
The Iron Age is a period in the history of primitive society, characterized by the spread of iron metallurgy and the manufacture of iron tools. Bronze Age civilizations go beyond the history of primitive society; other peoples' civilization takes shape during the Iron Age.
The term "Iron Age" is usually applied to the "barbarian" cultures of Europe that existed simultaneously with the great civilizations of antiquity (Ancient Greece, Ancient Rome, Parthia). The “barbarians” were distinguished from ancient cultures by the absence or rare use of writing, and therefore information about them has reached us either from archaeological data or from mentions in ancient sources. On the territory of Europe during the Iron Age, M. B. Shchukin identified six “barbarian worlds”:
- Proto-Germans (mainly Jastorf culture + southern Scandinavia);
- mostly Proto-Baltic cultures of the forest zone (possibly including Proto-Slavs);
- proto-Finno-Ugric and proto-Sami cultures of the northern forest zone (mainly along rivers and lakes);
- steppe Iranian-speaking cultures (Scythians, Sarmatians, etc.);
- pastoral-agricultural cultures of the Thracians, Dacians and Getae.
History of the development of public relations
The first tools of human labor were a chipped stone and a stick. People earned their livelihood by hunting, which they did together, and gathering. Communities of people were small, they led a nomadic lifestyle, moving around in search of food. But some communities of people who lived in the most favorable conditions began to move towards partial settlement.
The most important stage in human development was the emergence of language. Instead of the signal language of animals, which facilitates their coordination during the hunt, people were able to express in language the abstract concepts of “stone in general”, “beast in general”. This use of language led to the opportunity to teach offspring with words, and not just by example, to plan actions before the hunt, and not during it, etc.
Any spoils were divided among the entire group of people. Tools, household utensils, and jewelry were in the use of individual people, but the owner of the thing was obliged to share it, and in addition, anyone could take someone else’s thing and use it without asking (remnants of this are still found among some peoples).
A person’s natural breadwinner was his mother - at first she fed him with her milk, then generally took upon herself the responsibility of providing him with food and everything necessary for life. This food had to be hunted by men - the mother's brothers who belonged to her clan. Thus, cells began to form, consisting of several brothers, several sisters and the children of the latter. They lived in communal dwellings.
Experts now generally believe that during the Paleolithic and Neolithic times - 50-20 thousand years ago - the social status of women and men was equal, although previously it was believed that matriarchy first reigned.
At first, neighboring clans and tribes exchanged what nature gave them: salt, rare stones, etc. Both entire communities and individual people exchanged gifts; This phenomenon is called gift exchange. One of its varieties was “silent exchange”. Then tribes of farmers, cattle breeders and those who ran agricultural and livestock farming emerged, and between tribes with different economic orientations, and subsequently within tribes, the exchange of products of their labor developed.
Some researchers believe that tribes of hunters who did not accept an agrarian way of life began to “hunt” peasant communities, taking away food and property. This is how a dual system of producing rural communities and squads of former hunters robbing them developed. The leaders of the hunters gradually moved from raiding robbery of peasants to regular regulated exactions (tribute). For self-defense and to protect citizens from attacks by competitors, fortified cities were built. The last stage of pre-state development of society was the so-called military democracy.
Power and social norms in primitive society
The emergence of religion
Primitive tribes did not have special cult ministers; religious and magical rituals were performed primarily by the heads of clan groups on behalf of the entire clan, or by people whose personal qualities earned them a reputation as knowing the techniques of influencing the world of spirits and gods (healers, shamans, etc.). With the development of social differentiation, professional priests emerge, arrogating to themselves the exclusive right to communicate with spirits and gods.
see also
- Early history (protohistory)
Notes
Links
- Alekseev V.P., Pershits A.I. History of primitive society: Textbook. for universities for special purposes "Story". - M.: Higher. school, 1990
- "The transition from primitive society to class society: paths and options for development."
