Jupiter the most big planet in our solar system, with four large satellites and many small satellites that form a kind of miniature solar system. Jupiter is the size of a star; if it were about 80 times more massive, it would become a star rather than a planet.
On January 7, 1610, using his primitive telescope, astronomer Galileo Galilei saw four small “stars” near Jupiter. So he discovered Jupiter’s four largest satellites, which are called Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto. These four moons are known today as the Galilean moons.
Currently, 50 satellites of Jupiter have been described.
Io is the most volcanically active body in our world.
Ganymede is the largest planetary moon and the only one in the Solar System that has its own magnetic field.
Oceans of liquid may lie beneath the surface of Europa, and oceans of ice may also lie beneath the surface of Callisto and Ganymede.
When observing this planet, we can only see the surface of its atmosphere. The most visible clouds are composed of ammonia.
Water vapor is found below and can sometimes be seen as distinct spots in the clouds.
"Stripes", dark belts and light zones create strong west-east winds in Jupiter's upper atmosphere.

Visible even through a telescope is the Great Red Spot, a giant rotating cyclone that has been observed since the 1800s. IN last years three cyclones merged to form the Little Red Spot, which is half the size of the Great Red Spot.
The composition of Jupiter's atmosphere is similar - mostly hydrogen and helium. Deep in the atmosphere, high pressure, rising temperature, hydrogen turning into liquid.

At a depth of about one-third to the center of the planet, hydrogen becomes electrically conductive. In this layer, Jupiter's powerful magnetic field generates electricity, which is due to the rapid rotation of Jupiter. At the center of the planet, enormous pressure can support a solid core, approximately the size of Earth.
Jupiter's strongest magnetic field is almost 20,000 times stronger than Earth's magnetic field. Inside Jupiter's magnetosphere (the region where power lines magnetic field surrounds the planet from pole to pole) there are streams of charged particles.
The rings of Jupiter and the Moons are located inside the radiation belt of electrons and ions trapped magnetic field.
In 1979, the Voyager 1 spacecraft discovered 3 rings around Jupiter. The two rings are composed of small dark particles. The third ring, accordingly, consists of 3 more rings, which include microscopic debris and three satellites Amalthea, Thebe and Adrastea.
In December 1995 spaceship Galileo dropped a probe into Jupiter's atmosphere, which made the first direct measurements of the planet's atmosphere.
Moons of Jupiter
The planet Jupiter has four large moons, which are called the Galilean moons after they were discovered by the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei in 1610.
German astronomer Simon Marius claimed to have seen the moons around the same time, but he did not publish his observations and thus Galileo Galilei is credited as the discoverer.
These large satellites are called: Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto.
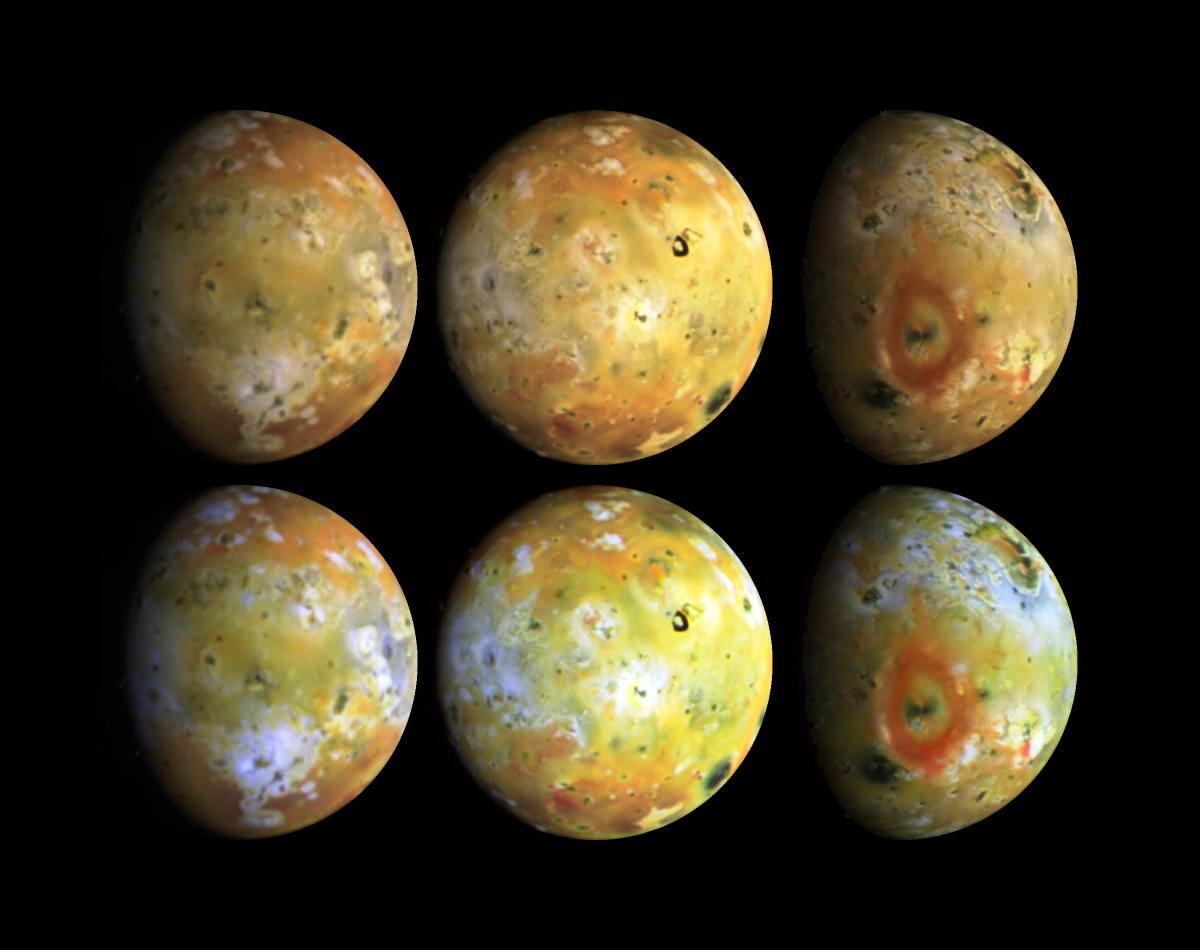
Jupiter's moon Io
Surface And about covered with sulfur in various colorful shapes.
As Io moves in a slightly elliptical orbit, Jupiter's enormous gravity causes "tides" in the moon's solid surface, up to 100 m high, producing enough energy for volcanic activity. Io's volcanoes erupt hot silicate magma.

Surfaces Europe consists mainly of water ice.
Europe is believed to have twice as much water as Earth. Astrobiologists put forward the theory that life is possible on the planet in a primitive form - in the form of bacteria, microbes.
Life forms have been found near underground volcanoes on Earth and in other extreme places that may be analogous to what may exist on Europa.

Ganymede is the largest satellite in the solar system (larger than the planet Mercury), it is also the only satellite with a magnetic field.
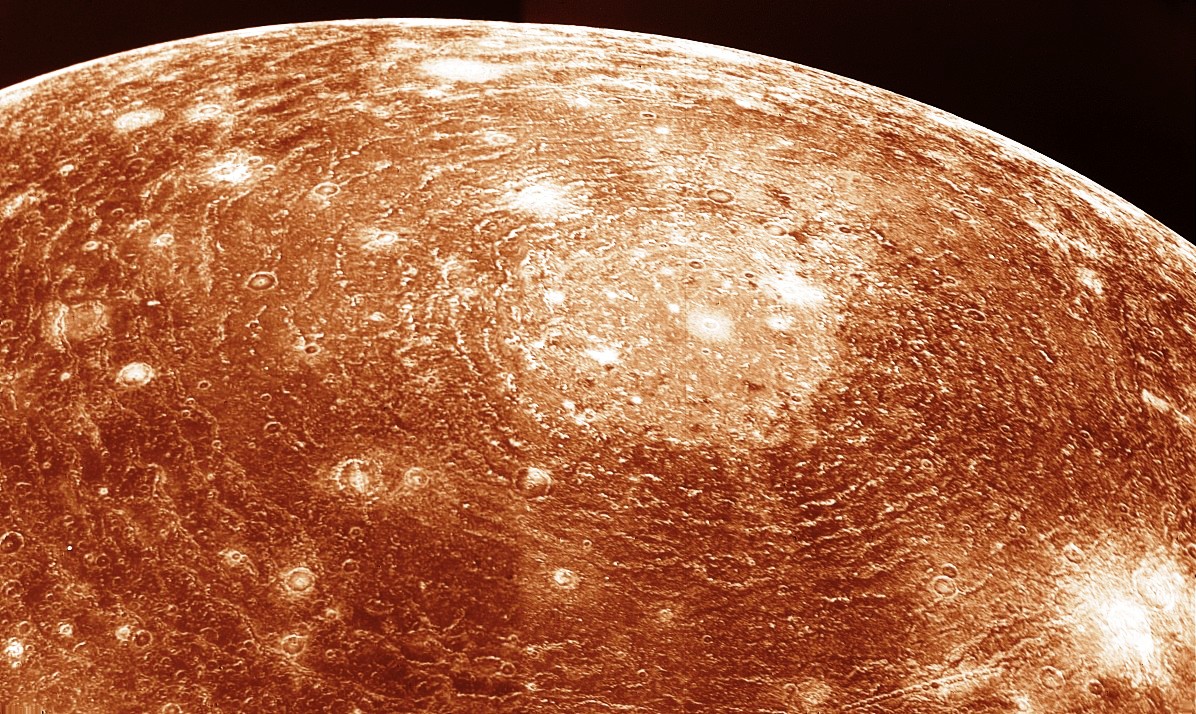
Surface Callisto very heavily filled with craters, as evidence early history Solar system. Several small craters may be active.
The planets Io, Europa and Ganymede have a layered structure (like Earth).
Io has a core, mantle, partially molten rock covered in rocks and sulfur compounds.
Europa and Ganymede have a core; shell around the core; a thick, soft layer of ice, and a thin crust of ice water.
Distance to orbit: 778,340,821 km (5.2028870 A.E.)
For comparison: 5,203 distances from the Sun to Earth
Perihelion (closest orbital point to the Sun): 740,679,835 km (4.951 A.U.)
For comparison: 5.035 distance from the Sun to the Earth
Apohelium (the farthest point in the orbit from the Sun): 816,001,807 km (5.455 A.U.)
For comparison: 5.365 times the distance from the Sun to the Earth
Stellar period of orbit (length of year): 11.862615 Earth years, 4 332.82 Earth days
Orbital circumference: 4887595931 km
For comparison: 5,200 Earth orbit distance
Average orbital speed: 47,002 km/h
For comparison: 0.438 Earth orbital speed
Orbital eccentricity: 0.04838624
For comparison: 2.895 Earth orbital eccentricity
Orbital inclination: 1.304 degrees
Average radius of Jupiter: 69911 km
For comparison: 10.9733 Earth radii
Equator length: 439,263.8 km
For comparison: 10.9733 lengths of the Equator
Volume: 1 431 281 810 739 360 km 3
For comparison: 1321,337 Earth volumes
Weight: 1 898 130 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 kg
For comparison: 317.828 Earth masses
Density: 1.326 g/cm3
For comparison: 0.241 Earth density
Area, more: 61,418,738,571 km2
For comparison: 120,414 Earth's area
Surface gravity: 24.79 m/s2
Second escape velocity: 216,720 km/h
For comparison: 5,380 escape velocity Earth
Stellar rotation period (day length): 0.41354 Earth days
For comparison: 0.41467 Earth rotation period
average temperature: -148°C
When describing this gas giant Superlatives are used very often. This is because Jupiter is not only the largest object in the entire solar system, but also the most mysterious. And also the first in mass, rotational speed and second in brightness. If you add together all the planets, moons, asteroids, comets of the system, Jupiter will still be larger than them combined. It is mysterious because the constituent components of this object are contained in the substance from which the entire solar system is made. And everything that happens on the surface and in the depths of the giant can be considered an example of the synthesis of materials that occurs during the formation of planets and galaxies.
If Jupiter were even more massive and larger, it could well be a “brown dwarf.”
This giant is a real defender of the Earth: all comets flying towards it are attracted by its powerful gravity.
History of discovery
Jupiter ranks second in the brightness ranking after Venus. Therefore, it, like the other four planets, can be seen directly from the surface of the Earth without any optical equipment. That is why not a single scientist can take credit for his discovery, which, apparently, belongs to even the most ancient tribes.
But the first scientist to begin systematic observation of the giant was the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. In 1610, he discovered the first satellites orbiting the planet. And they revolved around Jupiter. He named these four Ganymede, Io, Europa, Callisto. This discovery was the very first in the history of all astronomy, and the satellites later began to be called Galilean.
The discovery gave confidence to scientists who consider themselves heliocentrists, and allowed them to enter into the fight with adherents of other theories with renewed vigor. When optical instruments became more advanced, the size of the star was established, and the Great Red Spot, originally considered an island in the giant Jovian ocean, was discovered.

Research
In the period from 1972 to 1974, two Pioneer spacecraft visited the planet. They managed to observe the planet itself, its asteroid belt, record radiation and a powerful magnetic field, which allowed them to assume that there was a liquid inside the planet capable of conducting electric current. The second Pioneer spacecraft gave impetus to scientific "suspicions" that Jupiter has rings.
Launched in 1977, Voyagers reached Jupiter only two years later. It was they who sent to Earth the first, stunningly beautiful photographs of the planet, confirmed the presence of rings, and also allowed scientists to gain confidence in the idea that Jovian atmospheric processes are many times more powerful and grandiose than those on Earth.
In 1989, the Galileo spacecraft flew to the planet. But only in 1995 was he able to send a probe to the giant, which began collecting information about the atmosphere of the star. Subsequently, scientists were able to continue systematic studies of the giant using the Hubble orbital telescope.
The gas giant generates such strong radiation that spacecraft “do not risk” flying too close to it: on-board electronics may fail.

Characteristics
The planet has the following physical characteristics:
- The radius of the equator is 71,492 kilometers (error 4 kilometers).
- The radius of the poles is 66,854 kilometers (error 10 kilometers).
- Surface area - 6.21796⋅1010 km².
- Weight - 1.8986⋅1027 kg.
- Volume - 1.43128⋅1015 km³.
- Rotational period - 9.925 hours.
- Rings available
Jupiter is the largest, fastest and most dangerous object in our system due to its strong magnetic field. The planet has the most big number known satellites. Among other things, scientists believe that it was this gas giant that captured and retained untouched interstellar gas from the cloud that gave birth to our Sun.
But despite all these superlatives, Jupiter is not a star. To do this, it needs to have greater mass and heat, without which the fusion of hydrogen atoms and the formation of helium is impossible. To become a star, scientists believe, Jupiter must increase in mass by about 80 times. Then it will be possible to launch thermonuclear fusion. Still, Jupiter now produces some heat because it has a compression of gravity. This reduces the volume of the body, but contributes to its heating.
Movement
Jupiter is not only gigantic in size, but also in its atmosphere. It consists of 90 percent hydrogen and 10 percent helium. Because this object is a gas giant, the atmosphere and the rest of the planet are not shared. Moreover, when lowering down to the center, hydrogen and helium change their temperature and density. Because of this, Jupiter's atmosphere is divided into four parts:
- troposphere;
- stratosphere;
- thermosphere;
- exosphere.
Since Jupiter does not have the usual solid surface, scientists generally consider it to be the lower atmospheric boundary at the point where the pressure is one bar. As the altitude decreases, the temperature of the atmosphere also decreases, dropping to a minimum. The troposphere and stratosphere of Jupiter are separated by the tropopause, which is located at a distance of 50 kilometers above the so-called “surface” of the planet.
The giant's atmosphere contains small amounts of methane, ammonia, water, and hydrogen sulfide. These compounds are the reason for the formation of very picturesque clouds that can be seen from the surface of the Earth through telescopes. It is not possible to accurately determine the color of Jupiter. But from an artistic point of view, it is red and white with light and dark stripes.
The visible parallel bands of Jupiter are ammonia clouds. Dark streaks Scientists refer to them as poles, and the light ones as zones. And they alternate with each other. Moreover, only dark stripes consist entirely of ammonia. And what substance or compound is responsible for the light tone has not yet been established.
Jovian weather, like everything on this planet, can only be described using superlatives. The surface of the planet is filled with gigantic storms that do not stop for a second, constantly changing their shape, capable of increasing to a thousand kilometers in just a matter of hours. The winds on Jupiter blow at a speed of just over 350 kilometers per hour.
The most magnificent storm in the Universe is also present on Jupiter. This is the Great Red Spot. It has not stopped for several hundred Earth years, and its winds accelerate to 432 kilometers per hour. The size of the storm is capable of containing three Earths, they are so huge.

Satellites
The largest satellites of Jupiter, discovered by Galileo in 1610, became the first satellites in the history of astronomy. These are Ganymede, Io, Europa and Callisto. In addition to them, the most studied satellites of the giant are Thebe, Amalthea, the Rings of Jupiter, Himalia, Lysithea, and Metis. These bodies were formed from gas and dust - elements that surrounded the planet after the end of its formation process. Many decades passed before scientists discovered the remaining moons of Jupiter, of which there are sixty-seven today. No other planet has so many known satellites. And, probably, this number may not be final.
Ganymede is not only the largest moon of Jupiter, but also the largest in the entire solar system. If it revolved not around a gas giant, but around the Sun, scientists would classify this body as a planet. The diameter of the object is 5268 km. It exceeds the diameter of Titan by 2 percent and the diameter of Mercury by 8 percent. The satellite is located just over a million kilometers from the planet's surface, and is the only satellite in the entire system that has its own magnetosphere.
The surface of Ganymede consists of 60 percent unexplored ice strips and forty percent ancient ice “shell” or crust covered with countless craters. The age of the ice strips is three and a half billion years. They appeared due to geological processes, the activity of which is now questioned.
The main element of Ganymede's atmosphere is oxygen, which makes it similar to the atmosphere of Europa. The craters on the surface of the satellite are almost flat, without a central depression. This happened because the soft icy surface of the satellite continues to move slowly.
Jupiter's moon Io has volcanic activity, and the mountains on its surface reach a height of 16 kilometers.
As scientists suggest, on Europa under a layer surface ice There is an ocean in which water is in a liquid state.
Rings
Jupiter's rings are formed from dust, which is why they are so difficult to distinguish. The planet's satellites collided with comets and asteroids, resulting in material being thrown into space, which was captured by the planet's gravity. This is exactly how, according to scientists, the rings formed. It is a system consisting of four components:
- Torus or Halo (thick ring);
- Main ring (thin);
- Spider ring 1 (transparent, made of Thebe material);
- Spider ring 2 (transparent, made of Amalthea material);
The visible part of the spectrum, close to infrared, makes the three rings appear red. The Halo Ring is blue or almost neutral in color. The total mass of the rings has not yet been calculated. But there is an opinion that it ranges from 1011 to 1016 kilograms. The age of the Jovian ring system is also not precisely known. Presumably they have existed since the formation of the planet was finally completed.

Every summer evening, looking at the southern sky, you can see a very bright star with a reddish or orange tint. This is the planet Jupiter - the largest planet in the solar system.
Jupiter is the king among all the planets. It is in its fifth orbit, counting from the Sun, and we owe much of our quiet existence to it. Jupiter belongs to the gas giant planets, and its radius is 11.2 times greater than that of Earth. In terms of mass, it is almost 2.5 times heavier than all other planets combined. Jupiter has 67 known moons, some very small and some very large.
So Jupiter is the largest planet, with the largest mass, the strongest gravitational field, and the greatest influence in the solar system. In addition, it is one of the simplest and most beautiful objects to observe.
Of course, it is incorrect to talk about the discovery of this planet, because the planet Jupiter looks like the brightest star in the sky. That is why it has been known since ancient times, and there simply is not and cannot be a discoverer here.
Another thing is that Galileo Galilei in 1610 was able to examine the four largest satellites of Jupiter through his primitive telescope, and this was a discovery. But that's another story that applies to satellites. Subsequently, dozens more of them were discovered, both through telescopes and with the help of space probes.
The largest planet in the solar system undoubtedly has outstanding characteristics. In fact, this planet is so different from our tiny Earth that interesting facts quite a lot about Jupiter. Here are some of them:
- The planet Jupiter is very massive. Its mass is equal to 318 Earth's. Even if you take all the other planets and mold them into one lump, then Jupiter will be 2.5 times heavier than it.
- The volume of Jupiter would fit 1,300 planets like Earth.
- Gravity on Jupiter is 2.5 times greater than Earth's.
- The metal core of Jupiter is heated to 20 thousand degrees.
- Jupiter emits more heat than it receives from the Sun.
- Jupiter will never be a star; it does not have enough mass for this. For a thermonuclear reaction to begin in its depths, Jupiter needs to increase its mass by 80 times. This amount of matter cannot be accumulated in the Solar System, even if all the planets, their satellites, asteroids, comets, and all the small debris are collected together.
- Jupiter is the fastest rotating planet in the solar system. Despite its enormous size, it makes a full revolution in less than 10 hours. Due to its rapid rotation, Jupiter is noticeably flattened at the poles.
- The thickness of the clouds on Jupiter is only about 50 km. The cloud layer looks very powerful. All these huge storms and colored stripes thousands of kilometers in size are actually located in a small interval of thickness. They consist mainly of ammonia crystals - the lighter ones are located lower, and those that rise up become darker due to solar radiation. Under the cloud layer there is a mixture of hydrogen and helium of varying densities up to the metallic state.
- The Great Red Spot was first discovered by Giovanni Cassini back in 1665. This giant storm existed even then, that is, it is already at least 350-400 years old. True, over the past 100 years it has halved, but it is the largest and longest-lived storm in the solar system. Other storms last only a few days.
- Jupiter has rings; they were discovered after the well-known rings of Saturn and the much smaller rings of Uranus. Jupiter's rings are very faint. Perhaps they are formed from material that was ejected from satellites during meteorite impacts.
- Jupiter has the most powerful magnetic field of all the planets, 14 times stronger than Earth's. There is a theory that it is generated by a huge metal core rotating in the center of the planet. This magnetic field accelerates solar wind particles to almost the speed of light. Therefore, there are very powerful radiation belts near Jupiter that can damage the electronics of spacecraft, which makes it dangerous to get close to it.
- Jupiter has a record number of satellites - 79 were known in 2018. Scientists believe that there may be many more of them and not all have been discovered yet. Some are the size of the Moon, and some are just pieces of rock several kilometers in size.
- Jupiter's moon Ganymede is the largest moon in the solar system. Its diameter is 5260 km, which is 8% larger than even Mercury and 51% larger than the Moon. That is, it is practically a planet.
- Jupiter, with its gravity, protects us from many dangers in the form of comets and asteroids, deflecting their orbits. He practically cleaned out the interior of the solar system, providing us with enough free space. Comets and asteroids penetrating towards us sooner or later change their orbit under the influence of Jupiter to one that is more rounded and safer for the Earth.
- Jupiter can be easily observed. This is the brightest star in the earth's sky after Venus and the Moon. Already with 8-10x binoculars you can see 4 of its Galilean satellites. And in a small telescope, Jupiter is visible as a disk, and you can even see the belts on it.
As you can see, the planet Jupiter is not some ordinary ball of gas. This is a whole world that has many secrets and mysteries that scientists are gradually unraveling. In fact, this planet with its satellites is a miniature solar system, where dozens of its own unique worlds exist. If you are interested, you can also learn a lot of interesting things about Jupiter from a short video:
Distance from Jupiter to the Sun
The orbit of the planet Jupiter is located much further from the Sun than the Earth's. If from the Earth to the Sun it is approximately 150 million kilometers, or 1 astronomical unit, then to Jupiter it is on average 778 million kilometers, or 5.2 AU. Jupiter's orbit is not very different from circular; the difference in distance from the Sun at its closest and farthest points is 76 million kilometers.
A year on Jupiter lasts 11.86 Earth years—that’s how long it takes this planet to make one revolution around the Sun. At the same time, once every 13 months, Jupiter finds itself in line with the Earth, and the distance between them is minimal - this is called opposition. This is the best time to observe Jupiter.
Once every 13 years, the Great Oppositions of Jupiter occur, when this planet, moreover, finds itself not only opposite the Earth, but also at the closest point of its orbit. This best time, when every astronomer, both professional and amateur, points his telescope at this planet.
The planet Jupiter has a very slight tilt, only about 3 degrees, and the seasons there do not change.
Characteristics of the planet Jupiter
Jupiter is a very curious planet that has little in common with the things we are familiar with.
Radius– about 70 thousand kilometers, which is 11.2 times the radius of the Earth. In fact, due to its rapid rotation, this gas ball has a rather flattened shape, so its radius at the poles is about 66 thousand kilometers, and at the equator - 71 thousand kilometers.
Weight- 318 times the mass of the Earth. If you collect all the planets, comets, asteroids and other bodies of the Solar System in one heap, then Jupiter will be 2.5 times heavier than this heap.
Rotation time at the equator - 9 hours 50 minutes 30 seconds. Yes, this giant ball makes a full revolution around its axis in less than 10 hours, that’s exactly the length of a day there. But it is a ball of gas, not solid, and it rotates like a liquid. Therefore, in middle latitudes the rotation speed is different; the revolution there occurs in 9 hours 55 minutes 40 seconds. So the length of the day depends on the location. In addition, we can track the rotation of the planet only by clouds in the upper atmosphere, and not by surface landmarks, which are not there, just as there is no surface itself.
Surface area- 122 times larger than the earth’s, but this surface is not solid, and there is absolutely nowhere to land there. Yes, and there is no clear boundary. When descending to Jupiter, the gas will simply condense under pressure - at first it will be just a gaseous atmosphere, then something like a very rich fog, smoothly flowing into a completely liquid environment.
A magnetic field The planet Jupiter in the system is the most powerful, it is 14 times stronger than the Earth. The radiation from it is such that even space probes cannot withstand it for a long time without equipment breakdowns.
Atmosphere Jupiter, at least its upper layers, consists mainly of hydrogen (90%) and helium (10%). It also contains methane, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, water and other impurities. It has not yet been possible to study the deep layers reliably. Red phosphorus and its compounds are primarily what give Jupiter its red appearance. Enjoy virtual, eerily beautiful views of the atmosphere of the planet Jupiter:
Core Jupiter has a temperature of about 3000 K and consists of molten metal, in particular metallic hydrogen. The core size is larger than the Earth.
Acceleration free fall on the planet Jupiter will be approximately 2.5g.
What would await an observer who dared to approach Jupiter? At first there would be wonderful views of the planet, satellites, perhaps even the rings of the planet could be seen. Then, when approaching the planet, our daredevil would be killed by radiation. If his mortal body does not remain in eternal orbit and does enter the atmosphere, then fire, enormous pressure, and a long fall of what remains awaits him there. Or perhaps it won’t be a fall, but carrying the remnants at the behest of a hurricane, until chemical composition the atmosphere will not decompose them into individual molecules.
Jupiter's Great Red Spot

One of the most curious phenomena of Jupiter, which can be observed even with an average telescope, is the Great Red Spot, which is visible on the surface of the planet, and which rotates with it. Its dimensions (they are not constant) are approximately 40 thousand kilometers in length and 13 thousand kilometers in width - the entire Earth could fit into this giant hurricane!

Comparative sizes of the Great Red Spot on Jupiter.
Observations of this phenomenon have been ongoing for 350 years, and since then the spot has not disappeared. For a long time it was believed that it was something solid on the surface of the planet, but Voyager 1 in 1979 took detailed photographs of Jupiter and clarified this issue. It turned out that the Great Red Spot is nothing more than an atmospheric vortex! And this is the largest hurricane in the solar system, which people have been seeing for 350 years, and no one knows how long it has existed. Although over the past 100 years the size of the spot has become half as large.
The rotation of the spot around its axis is 6 hours, and at the same time it rotates with the planet.
The winds blowing in this hurricane reach speeds of 500-600 km/h (about 170 m/s). Compared to this, our strongest earthly hurricanes are nothing more than a gentle, pleasant breeze. However, in the center of the spot, as in terrestrial hurricanes of this type, the weather is quite calm. By the way, the wind is much stronger.
In addition to the Great Red Spot, there are other similar formations on the planet Jupiter - hurricanes. They form in different areas and can exist for decades, gradually disappearing. Sometimes they collide with each other or even with the Great Red Spot, and then its brightness and size can change. The longest-lived vortices are formed in southern hemisphere, but why this is so is not clear.
Moons of Jupiter
The giant Jupiter has a very large retinue, as befits a real god. To date, 79 satellites are known, of various sizes and shapes - from huge ones, like the Moon, to pieces of rock several kilometers long, like asteroids. They all have names associated with the god Zeus-Jupiter in mythology. Scientists believe that there may be even more satellites, although this is already a record number among all the planets in the solar system.
Since Galileo Galilei discovered the first and largest moons of Jupiter in 1610, Ganymede and Callisto have been the only ones known. They can be seen even with binoculars, and in a small telescope they are visible quite clearly.
Each of these moons of Jupiter is very interesting and represents a unique world. On some, scientists suggest the presence of conditions for the development of life, and even probe projects are being developed to study them in more detail.
In the 70s of the last century, astronomers already knew 13 satellites, and, flying past Jupiter, they discovered three more. In the 90s, new powerful telescopes appeared, including the Hubble Space Telescope. Since then, dozens more small satellites of Jupiter have been discovered, many of which are only a few kilometers in size. It is, of course, impossible to detect them with an amateur telescope.
The future of Jupiter
Now the planet Jupiter is not included in the habitable zone, since it is located too far from the Sun and liquid water cannot exist on the surface of its satellites. Although its presence is assumed to be under the surface layer, so-called subsurface oceans may exist on Ganymede, Europa and Callisto.
Over time, the Sun will increase in size, approaching Jupiter. Gradually, the satellites of Jupiter will warm up and some of them will have quite comfortable conditions for the emergence and maintenance of life.
However, in 7.5 billion years, the Sun will turn into a huge red giant, the surface of which will be located only 500 million kilometers from Jupiter - three times closer than from the Earth to the Sun now. The Earth and even by that time will have long been swallowed up by our swollen star. And Jupiter itself will turn into a planet of the “hot Jupiter” type - a gas ball heated to 1000 degrees, which itself will glow. Its rocky companions will be burnt pieces of stone, and the icy ones will disappear altogether.
But by that time, more favorable conditions will arise on the satellites, one of which is, and now represents a whole organic factory with a thick atmosphere. Perhaps then it will be the turn for new forms of life to appear there too.
Observing Jupiter
This planet is very convenient for novice amateur astronomers. It is visible in the southern part of the sky, and it rises quite high above the horizon. In terms of brightness, Jupiter is only inferior. The most convenient moments for observations are oppositions, when the planet is closest to Earth.
Oppositions of Jupiter:
Observing the planet Jupiter is interesting even with binoculars. 8-10x magnification in dark night will allow you to see 4 Galilean satellites - Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto. At the same time, the planet’s disk becomes noticeable and does not look like just a point, like other stars. Details, of course, are not visible through binoculars at such magnifications.

If you equip yourself with a telescope, you can see much more. For example, the 90 mm Sky Watcher 909 refractor, already with a complete 25 mm eyepiece (36x magnification), allows you to see several stripes on the disk of Jupiter. A 10 mm eyepiece (90x) will allow you to see a little more detail, including the Great Red Spot, shadows from satellites on the planet’s disk.
Larger telescopes will, of course, allow us to see the details of Jupiter in more detail. Details in the planet's belts will become visible and fainter satellites can be seen. With a powerful tool you can get some good pictures. It is useless to use a telescope with a diameter of more than 300 mm - atmospheric influences will not allow you to see more details. Most amateur astronomers use a diameter of 150 mm or more to observe Jupiter.
For greater convenience, you can use blue or blue filters of blue color. With them, the Great Red Spot and belts are visible in more contrast. Light red filters help you see blue details better, while yellow filters help you see polar areas better. With green filters, cloud belts and the Great Red Spot look more contrasting.
The planet Jupiter is very active; changes are constantly occurring in the atmosphere. It makes a full revolution in less than 10 hours, which allows you to see many changing details on it. Therefore, this is a very convenient object for first observations, even for those who have a rather modest instrument.
Planets of the Solar System
Characteristics of the planet:
- Distance from the Sun: ~ 778.3 million km
- Planet diameter: 143,000 km*
- Day on the planet: 9h 50min 30s**
- Year on the planet: 11.86 years***
- t° on the surface: -150°C
- Atmosphere: 82% hydrogen; 18% helium and minor traces of other elements
- Satellites: 16
* diameter along the planet's equator
**period of rotation around its own axis (in Earth days)
***period of orbit around the Sun (in Earth days)
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun. It is located at a distance of 5.2 astronomical years from the Sun, which is approximately 775 million km. The planets of the Solar System are divided by astronomers into two conditional groups: terrestrial planets and gas giants. The largest planet from the group of gas giants is Jupiter.
Presentation: planet Jupiter
The size of Jupiter exceeds the size of the Earth by 318 times, and if it were even larger by about 60 times, it would have every chance of becoming a star due to a spontaneous thermonuclear reaction. The planet's atmosphere is approximately 85% hydrogen. The remaining 15% is mainly helium with admixtures of ammonia and sulfur and phosphorus compounds. Jupiter's atmosphere also contains methane.

Using spectral analysis, it was found that there is no oxygen on the planet, therefore, there is no water - the basis of life. According to another hypothesis, there is still ice in the atmosphere of Jupiter. Perhaps no planet in our system causes so much controversy in the scientific world. Especially many hypotheses are associated with internal structure Jupiter. Recent studies of the planet using spacecraft have made it possible to create a model that allows high degree reliability to judge its structure.
Internal structure

The planet is a spheroid, quite strongly compressed from the poles. It has a strong magnetic field that extends millions of kilometers beyond its orbit. The atmosphere is an alternation of layers with different physical properties. Scientists suggest that Jupiter has a solid core 1 - 1.5 times the diameter of the Earth, but much denser. Its presence has not yet been proven, but it has not been refuted either.
Atmosphere and surface

The upper layer of Jupiter's atmosphere consists of a mixture of hydrogen and helium gases and has a thickness of 8 - 20 thousand km. In the next layer, whose thickness is 50 - 60 thousand km, due to increased pressure gas mixture turns into a liquid state. In this layer, the temperature can reach 20,000 C. Even lower (at a depth of 60 - 65 thousand km) hydrogen transforms into a metallic state. This process is accompanied by an increase in temperature to 200,000 C. At the same time, the pressure reaches fantastic values of 5,000,000 atmospheres. Metallic hydrogen is a hypothetical substance characterized by the presence of free electrons and conducts electric current, as is characteristic of metals.
Moons of the planet Jupiter

The largest planet in the solar system has 16 natural satellites. Four of them, which Galileo spoke about, have their own unique world. One of them, the satellite Io, has amazing landscapes of rocky formations with real volcanoes on which the Galileo apparatus, which studied the satellites, captured a volcanic eruption. The largest satellite in the Solar System, Ganymede, although smaller in diameter than the satellites of Saturn, Titan and Neptune, Triton, has an icy crust that covers the surface of the satellite with a thickness of 100 km. There is an assumption that there is water under the thick layer of ice. Also, a hypothesis is put forward about the existence of an underground ocean on the Europa satellite, which also consists of a thick layer of ice; faults are clearly visible in the photographs, as if from icebergs. And the oldest inhabitant of the Solar System can rightfully be considered Jupiter’s satellite Calisto; there are more craters on its surface than on any other surface of other objects in the Solar System, and the surface has not changed much over the last billion years.
Jupiter is the fifth planet in distance from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. Just like Uranus, Neptune and Saturn, Jupiter is a gas giant. Humanity has known about him for a long time. Quite often there are references to Jupiter in religious beliefs and mythology. In modern times, the planet received its name in honor of the ancient Roman god.
By scale on Jupiter atmospheric phenomena much superior to those on earth. The most remarkable formation on the planet is considered to be the Great Red Spot, which is a giant storm known to us since the 17th century.
The approximate number of satellites is 67, of which the largest are: Europa, Io, Callisto and Ganymede. They were first discovered by G. Galileo in 1610.

All studies of the planet are carried out using orbital and ground-based telescopes. Since the 70s, 8 NASA probes have been sent to Jupiter. During the great oppositions, the planet was visible to the naked eye. Jupiter is one of the brightest objects in the sky after Venus and the Moon. And the satellites and the disk itself are considered the most popular for observers.
Observations of Jupiter
Optical range
If you consider an object in the infrared region of the spectrum, you can pay attention to the He and H2 molecules, and the lines of other elements become noticeable in the same way. The quantity H speaks about the origin of the planet, and internal evolution can be learned through the qualitative and quantitative composition of other elements. But helium and hydrogen molecules do not have a dipole moment, which means that their absorption lines are not visible until they are absorbed by impact ionization. Also, these lines appear in the upper layers of the atmosphere, from where they are not able to carry data about deeper layers. Based on this, the most reliable information about the amount of hydrogen and helium on Jupiter can be obtained using the Galileo apparatus.

Regarding the remaining elements, their analysis and interpretation are very difficult. It is impossible to say with complete certainty about the processes taking place in the planet’s atmosphere. The chemical composition is also a big question. But, according to most astronomers, all processes that can affect the elements are local and limited. From this it turns out that they do not cause any special changes in the distribution of substances.
Jupiter emits 60% more energy than it consumes from the Sun. These processes affect the size of the planet. Jupiter decreases by 2 cm per year. P. Bodenheimer in 1974 put forward the opinion that at the time of its formation the planet was 2 times larger than it is now, and the temperature was much higher.

Gamma range
The study of the planet in the gamma-ray range concerns the aurora and the study of the disk. The Einstein Space Laboratory recorded this in 1979. From Earth, the aurora regions in ultraviolet and X-rays coincide, but this does not apply to Jupiter. Earlier observations established a pulsation of radiation with a periodicity of 40 minutes, but later observations showed this dependence much worse.

Astronomers had hoped that using the X-ray spectrum, the auroral lights on Jupiter would be similar to those of comets, but Chandra observations refuted this hope.
According to the XMM-Newton space observatory, it turns out that the disk's gamma-ray emission is solar X-ray reflection of radiation. Compared to the aurora, there is no periodicity in the intensity of the radiation.
Radio surveillance
Jupiter is one of the most powerful radio sources in the Solar System in the meter-decimeter range. Radio emission is sporadic. Such bursts occur in the range from 5 to 43 MHz, with an average width of 1 MHz. The duration of the burst is very short - 0.1-1 seconds. The radiation is polarized, and in a circle it can reach 100%.

The radio emission of the planet in the short-centimeter-millimeter range is purely thermal in nature, although, in contrast to the equilibrium temperature, the brightness is much higher. This feature indicates the flow of heat from the depths of Jupiter.
Gravitational potential calculations
Analysis of spacecraft trajectories and observations of the movements of natural satellites show the gravitational field of Jupiter. It has strong differences in comparison with the spherically symmetrical one. As a rule, the gravitational potential is presented in expanded form using Legendre polynomials.

The Pioneer 10, Pioneer 11, Galileo, Voyager 1, Voyager 2 and Cassini spacecraft used several measurements to calculate the gravitational potential: 1) transmitted images to determine their location; 2) Doppler effect; 3) radio interferometry. Some of them had to take into account the gravitational presence of the Great Red Spot when making measurements.
In addition, when processing the data, it is necessary to postulate the theory of motion of Galileo’s satellites orbiting around the center of the planet. Taking into account acceleration, which is non-gravitational in nature, is considered a huge problem for accurate calculations.

Jupiter in the Solar System
The equatorial radius of this gas giant is 71.4 thousand km, thereby 11.2 times greater than Earth’s. Jupiter is the only planet of its kind whose center of mass with the Sun is located outside the Sun.

The mass of Jupiter exceeds the total weight of all planets by 2.47 times, the Earth - by 317.8 times. But it is 1000 times less than the mass of the Sun. The density is very similar to the Sun and 4.16 times less than that of our planet. But the force of gravity is 2.4 times greater than that of Earth.
Planet Jupiter as a “failed star”
Some studies of theoretical models have shown that if Jupiter's mass were slightly greater than it actually is, the planet would begin to shrink. Although small changes would not particularly affect the radius of the planet, provided that if the actual mass were quadrupled, the planetary density increased so much that the process of shrinking in size began due to the action of strong gravity.

Based on this study, Jupiter has the maximum diameter for a planet with a similar history and structure. Further increases in mass resulted in continued contraction until Jupiter, through star formation, became a brown dwarf with 50 times its current mass. Astronomers believe that Jupiter is a “failed star,” although it is still not clear whether there is a similarity between the formation process of the planet Jupiter and those planets that form binaries star systems. Early evidence suggests that Jupiter would have to be 75 times more massive to become a star, but the smallest known red dwarf is only 30% larger in diameter.
Rotation and orbit of Jupiter
Jupiter from Earth has an apparent magnitude of 2.94m, making the planet the third brightest object visible to the naked eye after Venus and the Moon. At its maximum distance from us, the apparent size of the planet is 1.61m. The minimum distance from Earth to Jupiter is 588 million kilometers, and the maximum is 967 million kilometers.

Opposition between planets occurs every 13 months. It should be noted that once every 12 years the great opposition of Jupiter takes place; at the moment the planet is near the perihelion of its own orbit, while the angular size of the object from Earth is 50 arcseconds.
Jupiter is 778.5 million kilometers away from the Sun, while the planet makes a full revolution around the Sun in 11.8 Earth years. The greatest disturbance to the movement of Jupiter in its own orbit is made by Saturn. There are two types of compensation:
Age-old – it has been in effect for 70 thousand years. At the same time, the eccentricity of the planet’s orbit changes.
Resonant - manifests itself due to the proximity ratio of 2:5.

A peculiarity of the planet is that it has a great proximity between the orbital plane and the plane of the planet. On the planet Jupiter there is no change of seasons, due to the fact that the planet’s rotation axis is tilted 3.13°; for comparison, we can add that the Earth’s axis tilt is 23.45°.
The planet's rotation around its axis is the fastest among all the planets that are part of the Solar System. Thus, in the region of the equator, Jupiter rotates around its axis in 9 hours 50 minutes and 30 seconds, and in the middle latitudes this revolution takes 5 minutes and 10 longer. Due to this rotation, the radius of the planet at the equator is 6.5% greater than at middle latitudes.

Theories about the existence of life on Jupiter
A huge amount of research over time suggests that the conditions of Jupiter are not conducive to the origin of life. First of all, this is explained by the low water content in the planet’s atmosphere and the absence of a solid base of the planet. It should be noted that in the 70s of the last century, a theory was put forward that in the upper layers of Jupiter’s atmosphere there could be living organisms that live on ammonia. In support of this hypothesis, it can be said that the planet’s atmosphere, even at shallow depths, has a high temperature and high density, and this contributes to chemical evolutionary processes. This theory was put forward by Carl Sagan, after which, together with E.E. Salpeter, scientists performed a series of calculations that made it possible to derive three proposed forms of life on the planet:
- Floaters were supposed to act as huge organisms, the size of a large city on Earth. They are similar to a balloon in that they pump out helium from the atmosphere and leave behind hydrogen. They live in the upper layers of the atmosphere and produce molecules for nutrition on their own.
- Sinkers are microorganisms that are capable of multiplying very quickly, which allows the species to survive.
- Hunters are predators that feed on floaters.

But these are only hypotheses that are not confirmed by scientific facts.
Planet structure
Modern technologies do not yet allow scientists to accurately determine the chemical composition of the planet, but still the upper layers of Jupiter’s atmosphere have been studied with high accuracy. The study of the atmosphere became possible only through the descent of a spacecraft called Galileo, which entered the planet’s atmosphere in December 1995. This made it possible to accurately say that the atmosphere consists of helium and hydrogen; in addition to these elements, methane, ammonia, water, phosphine and hydrogen sulfide were discovered. It is assumed that the deeper sphere of the atmosphere, namely the troposphere, consists of sulfur, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen.

Inert gases such as xenon, argon and krypton are also present, and their concentration is greater than in the Sun. The possibility of the existence of water, dioxide and carbon monoxide is possible in the upper layers of the planet's atmosphere due to collisions with comets, as an example given by comet Shoemaker-Levy 9.
The reddish color of the planet is explained by the presence of compounds of red phosphorus, carbon and sulfur, or even due to organic matter that originated from exposure to electrical discharges. It should be noted that the color of the atmosphere is not uniform, which suggests that different areas consist of different chemical components.
Structure of Jupiter
It is generally accepted that the internal structure of the planet under the clouds consists of a layer of helium and hydrogen 21 thousand kilometers thick. Here the substance has a smooth transition in its structure from a gaseous state to a liquid state, after which there is a layer of metallic hydrogen with a thickness of 50 thousand kilometers. The middle part of the planet is occupied by a solid core with a radius of 10 thousand kilometers.

The most recognized model of the structure of Jupiter:
- Atmosphere:
- Outer hydrogen layer.
The lower part consists of a mixture of helium, hydrogen, ammonium and water. This layer is further divided into three:
- The top one is ammonia in solid form, which has a temperature of −145 °C with a pressure of 1 atm.
- In the middle is ammonium hydrogen sulfate in a crystallized state.
- The bottom position is occupied by water in the solid state and possibly even in the liquid state. The temperature is about 130 °C and the pressure is 1 atm.
The middle layer is represented by helium (10%) and hydrogen (90%).
- A layer consisting of hydrogen in a metallic state. Temperatures can vary from 6.3 thousand to 21 thousand Kelvin. At the same time, the pressure is also variable - from 200 to 4 thousand GPa.
- Stone core.
The creation of this model was made possible through the analysis of observations and research, taking into account the laws of extrapolation and thermodynamics. It should be noted that this structure does not have clear boundaries and transitions between neighboring layers, and this in turn suggests that each layer is completely localized, and they can be studied separately.

Atmosphere of Jupiter
Temperature growth rates across the planet are not monotonic. In the atmosphere of Jupiter, as well as in the atmosphere of the Earth, several layers can be distinguished. The upper layers of the atmosphere have the highest temperatures, and moving towards the surface of the planet, these indicators decrease significantly, but in turn the pressure increases.

The planet's thermosphere is losing most the heat of the planet itself, the so-called aurora is also formed here. The upper limit of the thermosphere is considered to be a pressure mark of 1 nbar. During the study, data were obtained on the temperature in this layer; it reaches 1000 K. Scientists have not yet been able to explain why the temperature here is so high.

Data from the Galileo spacecraft showed that the temperature of the upper clouds is −107 °C at a pressure of 1 atmosphere, and when descending to a depth of 146 kilometers, the temperature increases to +153 °C and a pressure of 22 atmospheres.
The future of Jupiter and its moons
Everyone knows that eventually the Sun, like any other star, will exhaust its entire supply of thermonuclear fuel, while its luminosity will increase by 11% every billion years. Due to this, the usual habitable zone will shift significantly beyond the orbit of our planet until it reaches the surface of Jupiter. This will allow all the water on Jupiter’s satellites to melt, which will begin the emergence of living organisms on the planet. It is known that in 7.5 billion years the Sun as a star will turn into a red giant, due to this Jupiter will gain new status and will become a hot Jupiter. In this case, the surface temperature of the planet will be about 1000 K, and this will lead to the glow of the planet. In this case, the satellites will look like lifeless deserts.

Moons of Jupiter
Modern data says that Jupiter has 67 natural satellites. According to scientists, we can conclude that there may be more than a hundred such objects around Jupiter. The planet's moons are named mainly after mythical characters who are in some way related to Zeus. All satellites are divided into two groups: external and internal. Only 8 satellites are internal, including the Galilean ones.

The first satellites of Jupiter were discovered back in 1610 by the famous scientist Galileo Galilei: Europa, Ganymede, Io and Callisto. This discovery confirmed the correctness of Copernicus and his heliocentric system.

The second half of the 20th century was marked by active study of space objects, including special attention deserves Jupiter. This planet has been explored using powerful ground-based telescopes and radio telescopes, but the most great achievements in this industry were obtained through the use of the Hubble telescope and the launch large quantity probes to Jupiter. Research is actively continuing at the moment, since Jupiter still holds many secrets and mysteries.
