Light ray in a gravitational field bends. The trajectory of a photon (light particle) in a stationary gravitational field in the general case is not a straight line (spatial geodesic).
Light is electromagnetic waves certain hour or so. The equations of electrodynamics were formulated for inertial reference systems, and in an inertial system in a void the light rays will be direct. The Newtonian theory of gravity does not provide any connection between the phenomena of electromagnetism and gravity, and therefore the prediction by Einstein's theory curvature of light raysthe gravitational field of the Sun was revolutionary and aroused great interest among physicists.
We must look for something that is between empty space and real physical matter, something invisible to the naked eye, but largely existing. The Rosicrucian Handbook tells us that the first form in which a spiritual entity concentrates on preparing for a material manifestation is electrons. When a spiritual entity gathers at very small focal points with an electric charge, we create electrons. Science tells us that such a cloud of free electrons will absorb all the light that comes into it.
The curvature of light rays by a gravitational field can be understood without computation, using the thought experiment suggested by Einstein. Let the elevator be held in the shaft by an electromagnet. There are holes on the opposite walls of the elevator at one level, and a light source is located opposite one of the holes on the shaft wall. As soon as the light source is turned on, the electromagnet is switched off and the elevator begins to fall freely. At the moment the light is turned on, the elevator becomes an inertial reference system in which the light propagates linearly. Therefore, the light beam entering the first hole will exit through the second. But during the passage of light distance L to the second wall of the elevator, equal L /c, the elevator goes down to the height h \u003dgL 2/2c 2 and the beam will exit from the second hole into the shaft at the same point at which it was emitted. In the reference system associated with the shaft, the beam will be bent.
It will not reflect or break light waves, and they cannot pass through a person. Therefore, the eyes of the observer will not notice anything, and a person surrounded by such a cloud is invisible. Since light is necessary for a person to see when there are no reflected or reflected light waves bouncing off a person and then falling into the observer’s retina, a person will not be seen under normal circumstances and will be invisible. How can this cloud be created consciously? There are certain references and descriptions of invisibility and its creation in the writings of secret societies, but most people do not have access to them.
The discovery of the curvature of light rays by a gravitational field was the first experimental test (except for the explanation of the precession of the orbit of Mercury) of the new theory of gravitation. Material from the site
During a total solar eclipse, stars become visible. If we photograph the starry sky in the vicinity of the Sun and compare the photograph obtained with a photograph of the same section of the starry sky taken at a different time, then, if there is a distortion of light rays, the position of the stars in the photographs will be different . Within the bounds of inevitable errors, the conclusions of the new theory of gravitation were confirmed.
You can go to India and become a student or student of an Indian guru or teacher to learn these methods. Patanjali, the author of the Yoga Sutra, who is one of the earliest sources, is trying to describe the process of this invisibility. He says that concentration and meditation can make the body unacceptable to other people, and when there is no direct contact with the light of the eyes, the body disappears. Researchers at Cornell University have designed, built, and demonstrated the first “mantle” that hides events over time.
The process is based on methods that distort electromagnetic fields, turning them into invisible coatings, but also uses the space-time duality in electromagnetic theory: diffraction and scattering of light in space are mathematically equivalent. Scientists used this theory to create a “temporary lens,” which can, for example, increase or contract over time. The weather cover uses two such lenses and places them so that one compresses a ray of light, and the other decomposes it.
On this page, material on the topics:
In contrast to Newton's theory, the curvature of the trajectory of a body moving in a gravitational field does not occur due to the action of a force, but due to the special properties of space. Inertia movement according to the general theory of relativity occurs in curved space-time.
Since all bodies, including light rays, move in the absence of forces along curved trajectories, we can assume that space itself is curved.
This leaves the beam relatively unchanged, but diffraction and distraction practically “hide” small events from the time line of the beam. For the observer, the light coming from the second lens is not distorted, as if no event had occurred. As a result, the space between the two lenses is a kind of space-time mantle that erases the changes that occur over this short period of time. At the moment, this phenomenon can last only 120 nanoseconds, and the theoretical maximum of this design is estimated at 120 microseconds.
The physical properties of space near gravitating masses differ from the properties of space far from them. “The structure of general relativity is such that the equations of the gravitational field ... are compatible only with such a movement of masses ... which satisfies the equations of conservation of energy and momentum” (Ya. B. Zel'dovich, ID Novikov General Theory of Relativity and Astrophysics). This means that if in the classical theory field equations existed separately from the equations of motion, then in the general theory of relativity the equations of the gravitational field contain the equations of motion.
Scientists refused to speculate on the possible uses of this “time masking”. However, technologies based on such distortion of electromagnetic fields have already been developed. Although the first “invisibility technologies” work only at microwave frequencies, physicists in recent years have discovered ways to develop “camouflage coatings” for visible light, sound, and sea waves. There are even those that make an object look like another. Transparency, such as the transparency of cells in matter, can be restored by transforming the cell structure.
Einstein in his theory generally abandoned the concept of gravity, replacing its effect with the curvature of world lines, the curvature of space-time itself. But the mathematical apparatus of the general theory of relativity turned out to be extremely complicated, and the corrections to the Newtonian theory of gravity obtained as a result of hard computing work are completely insignificant. Planck once said to Einstein: “Everything explained so well, why did you do this again?”
There are not many control experiments in which one can distinguish the predictions of Einstein's theory. An experimental verification of the general theory of relativity was proposed by its author. Einstein pointed out three effects: the deviation of a ray of light when passing near a massive body, the rotation of perihelion planets, the gravitational shift of the frequency of electromagnetic radiation.
When a ray of light passes through a gravitational field, its path should be curved (based on the principle of equivalence). Newton already posed this question: “Do bodies act on light at a distance and do not bend its rays with this action?” Here Newton has in mind the diffraction of the repulsion of light from bodies, which does not depend on their mass.
The most sensational of all tests of the general theory of relativity was carried out in 1919 during the complete eclipse of the Sun by the English astronomer A. Eddington. According to general relativity, gravity bends light rays. This curvature is so negligible that it cannot be detected using any laboratory experiment, but it can be measured by astronomers during a total eclipse of the sun. Sunlight is delayed by the moon and stars near the edge of the sun become visible. Light from them passes through the strongest part of the Sun's gravitational field. A shift in the apparent positions of these stars should indicate that the gravity of the Sun bends the path of light.
Newtonian physics also predicted the curvature of light in a gravitational field, but Einstein's equations gave twice as much deviation. The deviation of the light beam was close to Einstein's prediction, but the difficulties in making accurate measurements of the positions of the stars during the eclipse were much greater than Eddington had suggested.
Eddington made a presentation at a joint meeting of the Royal Society and the Astronomical Society in London. The President of the Royal Society, J.J. Thomson, in his opening speech said: “This is not the discovery of a remote island, but a whole continent of new scientific ideas. This is the greatest discovery since the time of Newton ”( Philipp Frank. Einstein, his life and times. N. Y., 1947, p. 141.).
At a conference of the Royal Society in 1962, a group of scientists came to the conclusion that since the difficulties are very great, observers of the eclipse should no longer try to make such measurements.
Ray of light passing in the distance  from the center of the Sun, deviates under the influence of gravity at an angle
from the center of the Sun, deviates under the influence of gravity at an angle
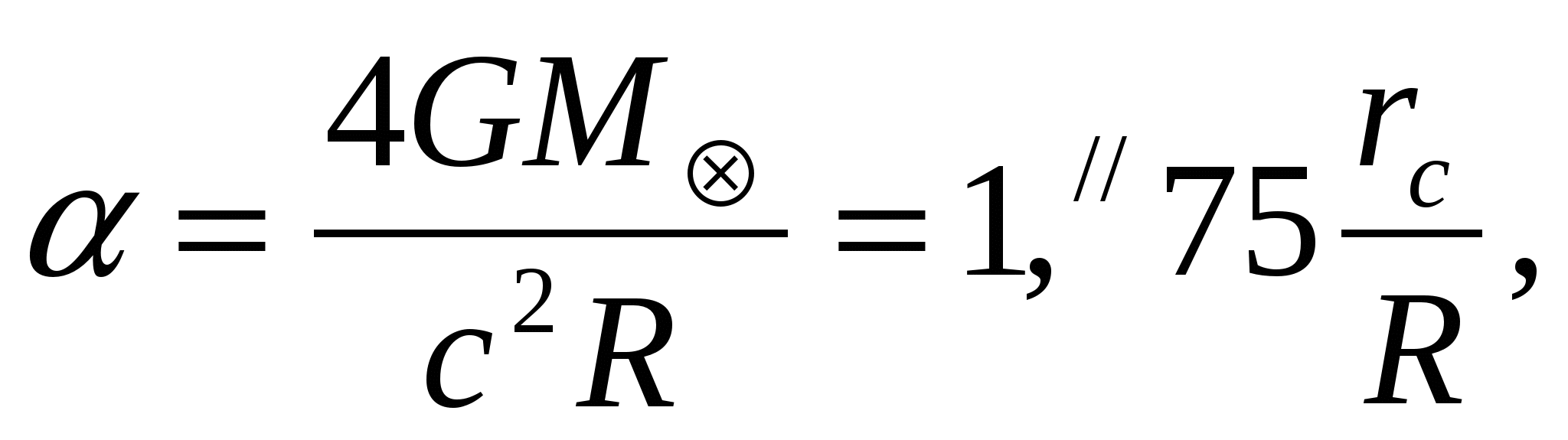 (1)
(1)
where 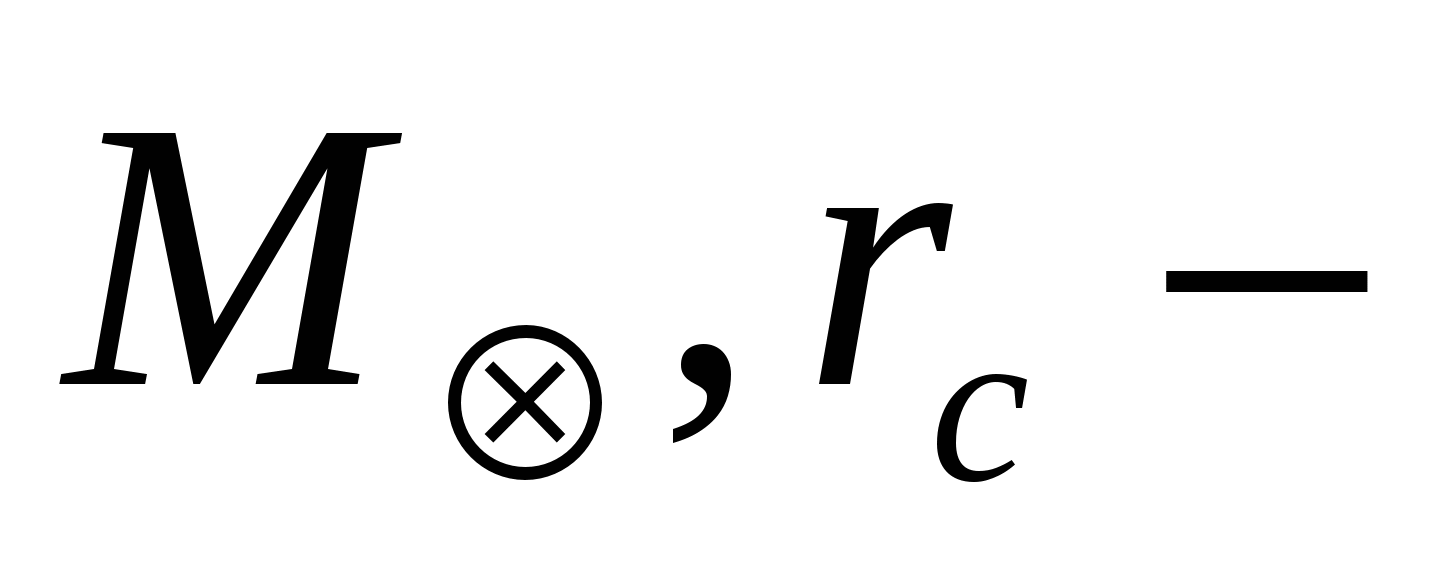 accordingly, the mass and radius of the sun.
accordingly, the mass and radius of the sun.
The maximum deviation should be observed for a ray passing at the edge of the solar disk, where 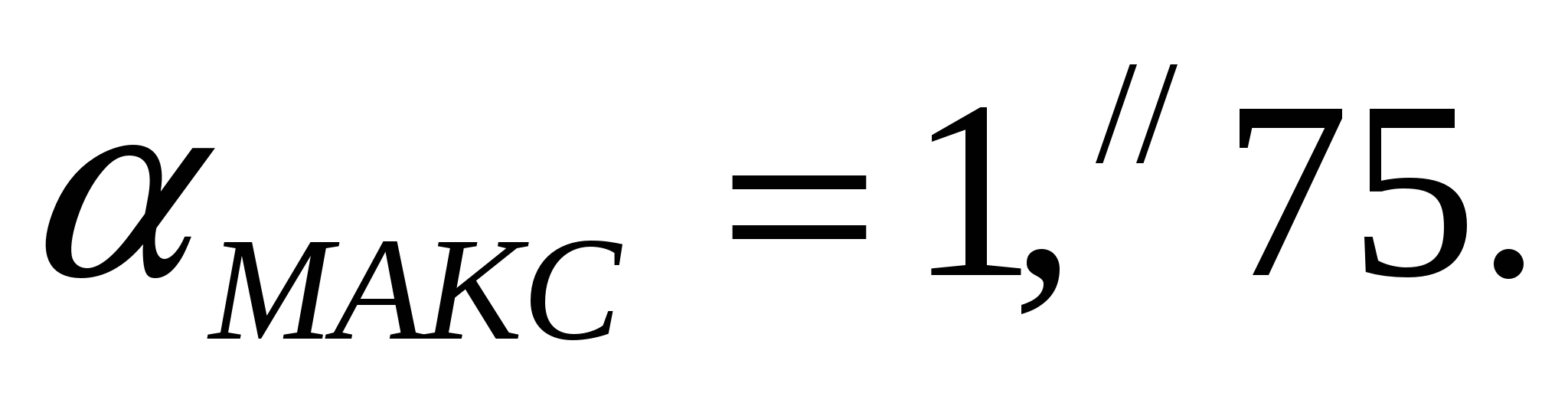 Observations during the 1952 eclipse gave
Observations during the 1952 eclipse gave 
