\u003e\u003e Predatory Squad
§ 74. Predatory unit
Most predatory mammals feed on large prey and therefore have very large fangs and large molars of a saw-shaped form. Cubs are born blind and helpless. In nature, carnivores play the role of regulators in the numbers of ungulates, rodents, and other animals. About 235 species belong to predators.
This is medium animalson high legs 139 They have an excellent sense of smell, they can find their prey in the wake and pursue it for a long time. Since the environment is changing rapidly, they are quick-witted and easily acquire new conditioned reflexes. 8 species live in the USSR: ordinary fox, arctic fox, wolf, raccoon dog, etc.
Common fox is common throughout our country, except the Far North. Lives in summer in a hole, where 4-6 foxes are born. Both parents take care of them. First, they bring the animals killed to the foxes, then the wounded, and then the living. So parents teach the foxes themselves to seize the prey. In the fall, the family breaks up, and in winter foxes live alone. Their fur at this time is thick and fluffy, so they sleep right in the snow, without climbing into a hole. The basis of nutrition is mouse-like rodents and other small vertebrates, and in autumn foxes willingly eat berries. In winter, they do not disdain carrion and often feed on garbage on the outskirts of settlements, they can also host poultry farm. The fox fur is beautiful and much appreciated.
Wolf.
This is a large predator weighing an average of about 50 kg, individual individuals reach 80 kg. Distributed throughout the country. Thanks to agility and strength, wolves can prey on animals that are superior in size to them. Large ungulate wolves try to hunt in packs. A flock of 5-12 wolves is formed because in the fall the brood does not fall apart. Each flock has its own habitat, within which it roams. Attacking domestic animals, wolves can cause great harm in areas of animal husbandry, especially since they usually try to kill as many animals as possible - in reserve. Cases of their attack on humans have also been noted, often these are rabid wolves. Therefore, in habitable areas, the number of wolves should be under human control.
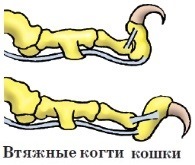
Their strongly bent claws are pulled into special bags when walking, therefore they remain always sharp. And they grab the prey first with claws, and then with teeth. Many have a weak sense of smell, and some are almost completely absent, but the hearing is excellent. Therefore, they prey on a prey or quietly sneak up on it and then take possession of it with a short throw.
There are 36 known living species of cats, 11 of them in the USSR: tiger (!), Leopard (!), Lynx (!), Snow leopard (!), Wild forest cat (!), Etc. 140 .
The tiger lives in South Asia and the USSR in the Far East. Large predator weighing up to 300 kg. It feeds on wild boars and deer, and can attack pets. The male does not take part in the upbringing of the young. Due to its small numbers, hunting for tigers is prohibited in the USSR.
Lynx - a resident of the taiga.
This is a fairly large beast, weighing about 15 kg. Lynx is well adapted for living in forests with deep snow: legs are long and paw pads are wide. The main food for her are hares and grouse birdsalso attacks roe deer and young deer.
Kunyi family.
For the most part, these are small predators with a long narrow body on low legs - rodents and birds make up the ability to penetrate narrow holes and feeding gaps. Many have beautiful and durable fur. In the USSR, the following are most common types of marten.
Marten and sable.
These are forest tree animals. Settled in hollows or burrows. Marten lives in the European part of the USSR, sable - beyond the Urals up to Kamchatka. They can hunt not only on the ground, but also on trees. They feed mainly on mouse-like rodents. Willingly eat berries and fruits.
Ferret and mink.
The ferret adheres to shrubs, edges. Sometimes it settles near settlements and, climbing into houses, can strangle a lot of birds here. But the basis of its nutrition are voles and mice. The mink keeps near water bodies, swims and dives well, preys on coastal and aquatic animals: frogs, rodents, snakes, crayfish, and sometimes fish.
The ermine and weasel are the smallest predators: the ermine is the size of a rat, and the weasel has a finger-thick body, and it easily penetrates the mouse minks.


Both animals turn white for the winter, but the ermine tip of the tail remains black. They feed mainly on mouse-like rodents.
The Bear family.
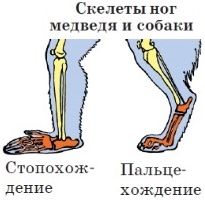
These are large animals with a massive physique, a large head, an elongated muzzle and powerful five-fingered stop-walking legs 142 . In the USSR, 3 species live: brown, white (!) And white-breasted.
Introduction
Common signs of the detachment
External and internal structure of predators
Habitat
Squad Families
Characteristic of squad families
List of references
Introduction
In this project, I wanted to talk about a rather complicated and, in my opinion, very interesting life of predators living on our planet Earth. Predators are very important in nature. They play the role of regulators of the number of ungulates, rodents and other animals. For humans, predators such as cats and dogs are pets. But do not forget that predators can bring great damage to the household. For example, animals such as the fox and the wolf, by stalking and stalking, attack defenseless domestic animals and eat them. For example, chickens, goats, rams, sheep, etc.
My life is also directly related to the animals of this squad. For example, a representative of the feline family lives in my house - the cat Vasya. Watching his behavior, I came to the conclusion that cats are excellent hunters, because they can perfectly disguise themselves and attack from shelter, hitting the victim with their agility by agility.
And now I would like to introduce you to my project, in which we will get acquainted in more detail with this view of the animal world.
Common signs of the detachment
 The animals included in the order of predators stand out among the remaining groups of mammals with an extraordinary variety. appearance, body size, biological features, adaptations to the environment, methods of transportation, etc. Most predatory animals lead a land-based lifestyle, but certain species, such as minks and otters, are inhabitants of fresh water bodies, and sea otters are marine animals. Predators feed not only on meat, but also on insects, invertebrates, and even plant foods.
The animals included in the order of predators stand out among the remaining groups of mammals with an extraordinary variety. appearance, body size, biological features, adaptations to the environment, methods of transportation, etc. Most predatory animals lead a land-based lifestyle, but certain species, such as minks and otters, are inhabitants of fresh water bodies, and sea otters are marine animals. Predators feed not only on meat, but also on insects, invertebrates, and even plant foods.
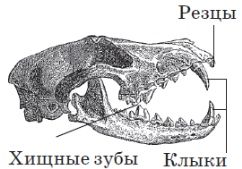
The body length of predators varies from 14 cm to 3 m, weight from 100 g to 1000 kg. The shape of the body can be elongated, flexible, massive, sometimes awkward. Some animals have tall, slender limbs, many others have short, clumsy. On each limb there are at least four fingers, and in bears and dogs there are five of them. All predators have claws, especially sharp ones in cats, in which (except for the cheetah) they can be drawn. In contrast, in some species of otters and in a sea otter, the claws turned into a kind of nails. Most predators have a long, often fluffy tail, and only in bears, a large panda and some others it is small and hidden in fur. Representatives of two genera of raccoons and wyverns have a grasping tail. The outer auricles in most species of predators are well developed, pointed, in the fenech and large-eared foxes are unusually large, while in the Arctic fox, ermine, weasels and others are barely protruded from the surrounding fur, and in the sea otter are underdeveloped. All predatory animals have a well-developed hairline, diverse in density, length, splendor, and color. Many species have a mottled coloration of the fur. In some northern species, a seasonal color change is observed - whitening of fur in winter (weasel, ermine, arctic fox) or its significant brightening (polar wolf).
External and internal structure of predators
The number of teeth of predators varies from 28 to 48. Among them are well developed, more or less curved, pointed fangs. The last upper preroot and the first lower molar in most species have turned into special predatory teeth. But the incisors are small. The high level of nervous activity characteristic of predators is ensured by the great perfection of the brain. It has well-developed hemispheres with three grooves, numerous convolutions, large olfactory lobes. Of the structural features internal organs a simple, gland-rich stomach can be noted. The intestinal length of carnivorous predatory species is relatively small. All predators, with the exception of hyenas, have a penis bone. Many species have well-developed anal glands, which emit a sharply smelling content, which serves to mark the territory, and sometimes (for a skunk) and to protect against enemies. The skin of predators is covered with hair. There are 2 types of wool - spine and undercoat.
Habitat
The vast majority of predatory animals leads a terrestrial lifestyle, inhabiting primarily forests, to a lesser extent - open spaces and mountains. Among forest predators, many climb trees well, but only some species of raccoon and civerora families are specially adapted for living in crowns. Some predators live near ponds, swim well and dive. Shelters of predatory animals are independently dug, sometimes very deep burrows, alien dwellings, as well as crevices of rocks, caves, niches among the roots of trees, hollows, piles of stones and windbreak, littered with snow in the North in winter. Often, one predator has several shelters, others manage with open dens and simple lying on the ground and in the snow.
Squad Families

Squad predatory


representative of the bear family
Characteristic of squad families
WOLF family (Canidae ) Large and medium sized animals, with a sharp muzzle, pointed auricles and a long fluffy tail. They are armed with strong, but blunt and non-retractable claws. The color of the coat is diverse: plain, mottled, spotted, sometimes very bright. Representatives of the family are distributed across all continents. They lead a single-family or group lifestyle. In most cases, they are monogamous.
This family includes wolves, foxes, arctic foxes, dogs, jackals, coyotes and many others.
Feline Family (Felidae) . Medium and large animals. The body is slim and flexible. The head is round. Fangs are long, curved. Pads are developed on the fingers. Feline - of all carnivores, they are better suited to obtaining animal food mainly by way of guard, more rarely, by persecution. They feed on the meat of their victims. Among feline there are excellent runners. They are all finger-oriented. They eat only animal food. Active all year round. They live mainly alone or in families.
This family includes cats, leopards, lions, cheetahs, panthers and etc.
Family of BEARS (Ursidae). Bears are the largest of modern predatory animals. All animals of this family have a powerful body, many with a high withers; paws strong, with large claws, five-fingered, stop-walking; the tail is short, barely visible from the fur; the head is massive, with small eyes and ears. The coat is dense, uniformly dyed in black, brown or white, not changing seasonally.
This family includes brown, polar bears,
COUNTY family (). Small and medium-sized animals. The body is elongated, legs are short.
This family includes martens sables, ferrets
Findings:
In conclusion, I would like to draw a few conclusions. During work, I got acquainted with very interesting, diverse and informative information. While working on the project, I learned a lot about the life, meaning and structure of predators. The work was interesting, exciting, and most importantly productive!
List of used literature:
1. M.A. Kozlov, “Biology. Animals. ”Textbook for grades 7-8, Moscow“ Enlightenment ”, 1990, pp. 256
2. A.G. Bannikov, P.A. Genkel, “Plants and Animals” Children's Encyclopedia, Moscow “Pedagogy”, 1973, p. 447
3. L. Yakhnina, A. Zaitseva, “Ecology”, encyclopedia, “Rusich”, 1998, p. -151
4. A.S. Barkov, I.B. Shustova, “Big Atlas of animals”, “ROSMEN”, 1998, p. 67
5. www.floranimal.ru
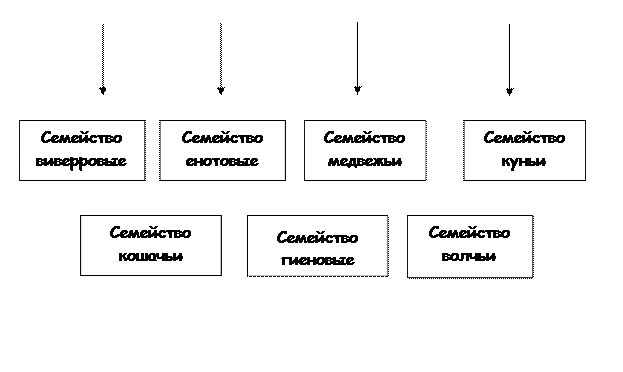
X search teeth - these are four molars, characterized by size and sharp, cutting tubercles.
Ost - This is thick, long hair that protects the skin from damage.
Undercoat - This is a short, soft hair that retains body heat.
Propagate once a year, are highly fertile.
Foot climb - when walking, they rely on the entire foot.
Predatory Squad (Carnivora)
This order includes wolves, foxes, arctic foxes, dogs, lions, tigers, leopards, lynxes, wild and domestic cats, sables, martens, ferrets, minks, otters, ermines, weasels, hyenas, bears. In total - about 280 species of animals, which are divided into seven families: Dog (Wolf), Feline, Bear, Kunyi and others. These are animals that lead a land-based lifestyle.
Predatory animals actively pursue their prey. For example, wolves drive a hare or a wild boar until the victim becomes weak. Lynxes, lions, tigers usually lie in wait for prey, and then suddenly attack.
The cerebral hemispheres are large, covered with furrows and convolutions. These are animals with a flexible spine, well-developed sense of smell and hearing. Five-fingered limbs are armed with claws. The hairline is well developed. Most of these animals feed on the meat of various animals, birds, fish. Some (like bears) have a richer diet.
 The teeth of predators are divided into incisors, fangs and molars. The most developed of them are fangs and four molars, which, unlike other molars, are called predatory . Predators kill and tear up prey with fangs, bite their muscles and tendons with molars, and cut meat from the bones of the animals they killed with cutters. The intestines of predators are shorter than those of herbivorous mammals, which is associated with the nutrition of easily digested food.
The teeth of predators are divided into incisors, fangs and molars. The most developed of them are fangs and four molars, which, unlike other molars, are called predatory . Predators kill and tear up prey with fangs, bite their muscles and tendons with molars, and cut meat from the bones of the animals they killed with cutters. The intestines of predators are shorter than those of herbivorous mammals, which is associated with the nutrition of easily digested food.
Predators lack clavicles. The forebrain has a large number of convolutions and furrows. They have well-developed sensory organs, and they have complex behaviors.
Brief description of families
Wolf (Dog) (about 30 species) - large and medium-sized animals with a sharp muzzle, pointed auricles, a long, fluffy tail, legs with blunt non-traction claws ( jackal , coyote , raccoon dog and etc.). They catch catch and grab on the run. This family includes wolves, foxes, arctic foxes, jackals.
The largest member of the family is ordinary wolf . It is distributed throughout Russia. The most numerous are wolves in places with free grazing of cattle on which they attack. Wolves prey on large animals (deer, wild boars) in groups, usually at night.
Common fox distributed as widely as the wolf. She chooses sparse forests, valleys, neighborhood villages. It settles in deep burrows, which it usually digs on the slopes of ravines. The fox feeds mainly on rodents.
In the tundra and forest-tundra lives arctic fox . He is smaller than a fox. In summer, fox fur has an earth-gray color, and in winter it is snow-white. Winter fox fur is warmer than summer. There are arctic foxes with a bluish coloration of fur. The soles of the fox's feet are completely covered with a brush of hard hair, and the short and rounded auricles are almost hidden in the wool, which saves them from frostbite during severe frosts. In summer, foxes feed on rodents, bird eggs, chicks and even partridges and other adult birds.

 Feline
(about 40 species) - medium and large in size predators with a slender, long, flexible body and a rounded head. Pads are developed on the toes of cats. Sharp bent claws are drawn into special grooves, so they do not blunt and do not knock when walking. Feline usually at go twilight and nightlife. Some species hunt alone, others (e.g.the lions
) - groups (prides).a lion
,
tiger
,
jaguar
,
cougar
- predators dangerous to humans. The number of cats is greatly reduced, in many countries they are protected.Cheetahs
tamed for hunting antelopes.wild cat
domesticated - all breeds of domestic cats originated from it.
Feline
(about 40 species) - medium and large in size predators with a slender, long, flexible body and a rounded head. Pads are developed on the toes of cats. Sharp bent claws are drawn into special grooves, so they do not blunt and do not knock when walking. Feline usually at go twilight and nightlife. Some species hunt alone, others (e.g.the lions
) - groups (prides).a lion
,
tiger
,
jaguar
,
cougar
- predators dangerous to humans. The number of cats is greatly reduced, in many countries they are protected.Cheetahs
tamed for hunting antelopes.wild cat
domesticated - all breeds of domestic cats originated from it.

Of the cats living in Russia, the most famous lynx - a large forest animal with a short body, high and strong legs, a short tail. It feeds on hares, hazel grouse and other animals. Climbing trees well; prey watches over.

The largest felinetiger and a lion . The tiger is a typical predator of South Asia. Leo is a resident of Africa and Southwest Asia.
In Russia, in the Far East, it occursussurian tiger which is listed in the Red Book.
 Bear
(7 species) - large animals of heavy physique. When walking, they rest on the entire foot. The most common member of the family is brown bearb
. It inhabits mixed and mountain forests. It feeds mainly on plant foods. Often it hunts large animals, catches fish, eats large insects. The bear runs fast, can climb trees, swim. For the winter falls into a winter dream. He sleeps most often in the den, which he arranges in the recesses under the inverted tree roots, in the crevices of the rocks.
Bear
(7 species) - large animals of heavy physique. When walking, they rest on the entire foot. The most common member of the family is brown bearb
. It inhabits mixed and mountain forests. It feeds mainly on plant foods. Often it hunts large animals, catches fish, eats large insects. The bear runs fast, can climb trees, swim. For the winter falls into a winter dream. He sleeps most often in the den, which he arranges in the recesses under the inverted tree roots, in the crevices of the rocks.
On the islands and the coast of the Arctic Ocean inhabits polar bear . He eats fish, seals. Only females fall into winter sleep.

The body weight of a brown bear is about 600 kg, white - about 1000 kg. The head of the bears is large, the auricles are small and rounded, the eyes are small. Sneaks up to production and at a speed of 50 km / h. Bears give birth to very small cubs: a brown bear in the den gives birth to a bear cub about 20 cm long and weighing 500 g.
In the southern part of the Far East and in America, herbivorous black bear . He arranges a den in the hollows of large trees or in caves.
Cunyi (about 70 species) - small and medium-sized animals, with an elongated body and short legs. The fur of most marten with a soft undercoat.
The smallest predator of this family is affection . She lives on the fringes of forests, lakeside, in ricks and outbuildings. It feeds on mice, voles. In winter, weasel is white, in summer it is brownish brown.
Ermine larger than affection. It can be distinguished by the dark brown tip of the tail. In the dark coniferous taiga lives sable . He climbs trees well, but leads mainly a terrestrial lifestyle. It feeds on rodents, birds, pine nuts. Fairly widespread martens , ferrets .

The largest representative of marten in Russia - badger - a resident of mixed forests. Most spends life in a hole, falling into a winter dream for six months.
Of the marten, leading an aquatic lifestyle, is widespread otter . She lives mainly near fresh water in burrows. It feeds mainly on fish.
Almost all cuns, especiallysable, mink, ermine andsea \u200b\u200botter , - fishing subject due to valuable fur.
Raccoons (7 species) - small animals, the body of which is covered with thick fluffy fur, the tail is long. Some species are hunted (fur is used). Seven species live in Southeast Asia and in America; in Europe acclimatizedraccoon .

Recent studies conducted several years ago based on comparative anatomy and DNA analysis have shown thatbig panda (bamboo bear) it refers not to raccoons, as previously thought, but to the bear family.
Viverra (about 75 species) - small slender animals with short legs and a long tail; many of them resemble martens in appearance. They feed on small animals, sometimes nuts. They live on land and trees in Africa, South Asia and Southwest Europe.Mongooses can eat poisonous snakes.
 Hyenas include 4 species of dog-like animals. The short torso in front is higher than in the back. They have a thick neck and a massive head. The body is covered with coarse hair, sometimes forming a mane.
Hyenas include 4 species of dog-like animals. The short torso in front is higher than in the back. They have a thick neck and a massive head. The body is covered with coarse hair, sometimes forming a mane.
Hyenas live in Africa, Central and Southwest Asia, inhabiting semi-deserts, steppes and savannahs. They lead a nocturnal lifestyle, feed on carrion, only occasionally attacking live animals. Known cases of attacks on children. They are kept alone, only with food they join in a flock.
Predatory animals play an important role in natural ecosystems: they prey on insectivorous and herbivorous birds and mammals, eat amphibians and reptiles. Large predators attack smaller representatives of their squad. The role of predators as regulators of the number of small rodents, including pests of cultivated plants, is great. Predators have a healing effect on prey populations, destroying diseased animals, as they are easier to get. By this they prevent the spread of mass diseases - epizootics.
Squad predatory
(Carnivora) *
* The predatory order includes about 270 living species. According to modern scientific views, this order also includes seals, walruses and sea lions, formerly united under the name "pinnipeds". Scientists divide the order of predatory into two suborders: cat-like and dog-like.
Hardly any other detachment of mammals represents such a wealth of forms as predatory. The size of these animals is very different - from very large to smallest, and they also differ in body structure. From a huge lion to a little caress - how many intermediate steps, how many differences in appearance! Here we can meet a beautifully painted graceful cat, and next to it - a clumsy hyena; slender, mobile wiverra with silky, smooth fur and a large furry dog; a heavy and clumsy bear and a quick, dodgy marten. Can these so different animals belong to the same order? Can they be joined together if some of them live on the earth, others climb trees, others feel at home only in the water? Despite the difference in appearance, all predators have much in common: the same way of life, habits, the same food and, as a result, the similar structure of the limbs, skeleton and teeth.
The limbs of predators in their length and thickness strictly correspond to the size of the body; on these limbs there are from four to five fingers with more or less developed - blunt or sharp, retractable or non-retractable - claws. All senses are highly developed. The teeth of animals in most cases are large enough, have sharp tubercles or a conical, acute shape and sit tightly in the jaws; with a closed mouth, a row of lower teeth is placed right behind the row of upper teeth. The teeth form an excellent cutting tool, and well-developed chewing muscles give this tool great strength. The stomach looks like a simple bag. The intestines are never very long, and sometimes even very short, the blind process of the intestines is poorly developed. At the anus there are sometimes special glands that secrete a strong-smelling liquid, which serves to protect against enemies, sometimes to lure prey, and sometimes they secrete a greasy mass that serves to lubricate the fur **.
* * One of the important functions of these glands is labeled by an individual hunting area with odorous marks.
Below we list the main external signs of predators. The body structure of these animals is very diverse - from short and thick in a bear to long and thin in a wyverra; the limbs are almost always medium in size with four or five fingers equipped with claws; head for the most part it is round, the tip of the nose is bare, eyes are large and keen, ears are usually erect, lips are surrounded by a mustache, and sometimes a beard. There are six small incisors and two long conical fangs in the mouth, both on the upper and lower jaws, which serve to grasp the prey. The posterior pseudo-rooted teeth of the upper jaw and the anterior real molar of the lower have a three-toothed and laterally compressed crown: these teeth serve mainly for cutting meat; other false-rooted teeth are also laterally compressed, but have one tooth each, and some real molars end with a flat apex for grinding food *.
* Fangs serve not only to hold, but often to kill prey. The shape of the molar crown can vary greatly depending on what the animal eats. For example, in bears, omnivores, eating a lot of plant food, they never form sharp peaks or edges and have a flattened tuberous surface (like pigs and monkeys).
The internal structure of the body of carnivores has several more or less clearly expressed common features. The skeleton, despite the lightness and beauty of the form, is very durable. The skull is elongated; that part of it where the brain is located is almost the same length as the muzzle, so that none of these parts practically prevails over the other. Large ridges and prominent seams on the skull, as well as very convex zygomatic arches serve as the basis for strong muscles, which, contracting, set in motion the lower jaw; eye cavities quite large; swelling of the parietal bone where the inner ear is placed is very noticeable; the nasal bones and cartilage are also well developed - all this indicates a good development of the organs of vision, hearing and smell. The spinal and cervical vertebrae have large processes; lumbar vertebrae often fuse together; the number of caudal vertebrae varies for different species of predators. The structure of the limbs depends on the lifestyle of the animal, but always indicates the strength and mobility of these parts of the body.
The limbs of a predator are sometimes short and thickened; this indicates that the animal breaks the ground well and leads an underground lifestyle. Sometimes these limbs are very long - such animals are excellent runners. In some predators, the fingers are connected by a swimming membrane - this is a sign of the aquatic life of the beast. Claws are sometimes retractable, this protects them when walking from abrasion, and when released, they serve as an excellent tool for grasping and tearing prey; in some animals, the claws do not retract, and therefore are not so sharp; in this case, they serve as a support for the legs, as well as for digging the ground and for climbing. If we talk about teeth, then the main role is played by very long fangs and sharp molars, the so-called carnivorous teeth; they serve for setting and tearing prey, as well as for cutting meat. The lower jaw is set in motion through the large muscles and thick tendons, contributing to the very strong and diverse movements of this part of the skull **.
* * The lower jaw of most predators is not capable of complex movements. On the contrary, a very strong jaw joint allows it to move only in one plane up and down. She can make lateral movements only in some omnivorous predators, eating a lot of plant food.
As already mentioned above, the sense organs in these animals are perfectly developed, but sometimes, as an exception, one of them is poorly developed, and then this shortcoming is rewarded by strongly developed other feelings.
In general, it cannot be said that in all predators one certain feeling is always developed stronger than the others; on the contrary, some have a more developed sense of smell, others have eyesight, others have hearing, and in other cases, touch also plays an important role. In most cases, two senses are most acute: the sense of smell and hearing; in more rare cases, hearing and vision.
The mental abilities of predators are quite consistent with the development of sensory organs: in this detachment you can find unusually smart animals, and therefore it is not surprising that they show a lot of cunning and dexterity, which are necessary for a successful hunt. Self-confidence makes animals bold and adventurous - these qualities in other animals are never as developed as in predators, but at the same time they cause some of the shortcomings of these so perfect creatures.
The place of residence and lifestyle of animals are directly related to their temper and body structure. Predators live and rule everywhere: on the earth and in the water in the same way as on the tops of trees; in the mountains, as in the plains; in the forest, as in the field; in the north, as in the south. Predators are divided into day and night animals: some are looking for prey in the sunlight, others at dusk, and others at dark night.
Some predators form societies, others prefer loneliness, some attack their prey openly, but most watch for it, hiding and not making the slightest noise, then attack unexpectedly, which gives them the opportunity to catch animals that are sometimes larger than the predators themselves. In such cases, predators try to hide in order not to frighten premature prey with their appearance, and only a few, aware of their weakness, seek escape in flight if they notice anything suspicious.
All predators feed on other animals and only as an exception eat fruits, seeds and other plant substances. Usually, predators are divided into omnivores and carnivores, but the first name is not entirely true, because omnivores still prefer a good piece of meat to any other food. It goes without saying that in terms of food, or, more precisely, in its prey, predators differ from each other in accordance with their place of residence, the region in which they live, body structure and lifestyle. Only a few species of the animal kingdom are not attacked and do not serve as prey for predators. The largest and most powerful representatives of this order feed mainly on mammals, without neglecting, however, other animals. Even a lion does not feed solely on mammals, the rest of the cats are even less legible; dogs, whose main food, though meat, are quite content with other foods. Among wiverres and martens, there are often those who eat exclusively fish or, just as eagerly, reptiles; Bears are usually called omnivores, and, indeed, they are equally willing to eat both plant and animal food. For vertebrate animals, carnivores are hunters or, rather, enemies, in the same way as for invertebrates. Predators find their prey on solid ground, in water, on tree branches, in the north, south, in high mountains and underground. Certain species of this detachment sow death everywhere, as they live it; the weak should serve as the prey of the strong, and no animal can be saved from the attack of a predator.
Some predatory mammals live, in the common opinion, in pairs, but some cats and martens only pair at certain times of the year, connecting together to feed, protect and protect cubs, but in many cases the father looks at his cubs as prey , and the mother has to drive him away from the lair when he accidentally finds him. In these cases, the mother is the only teacher. The number of cubs in one litter is very different, but rarely less than two. Almost always, cubs are born blind and at first very helpless, but then develop, as a rule, rather quickly. The mother thoroughly teaches them to catch prey and find the appropriate food and protects them until the babies can live independently. Only a few predators carry their cubs on their backs or hold them with their forelimbs; most carry them from place to place in the teeth.
Man lives with almost all predatory animals in open hostility, only a few he managed to tame and now uses their services. Most predators are considered, more or less fairly, dangerous animals, and therefore they are ruthlessly exterminated. The meat and fat of some animals of this detachment is eaten, the precious fur of others serves for human clothing, and, bearing in mind this benefit, we can, of course, excuse the hunt for them. Unfortunately, we often notice that a person, as a result of a blind desire to destroy, pursues not only harmless, but even useful predatory animals *.
Introduction
Common signs of the detachment
External and internal structure of predators
Habitat
Squad Families
Characteristic of squad families
List of references
Introduction
In this project, I wanted to talk about a rather complicated and, in my opinion, very interesting life of predators living on our planet Earth. Predators are very important in nature. They play the role of regulators of the number of ungulates, rodents and other animals. For humans, predators such as cats and dogs are pets. But do not forget that predators can bring great damage to the household. For example, animals such as the fox and the wolf, by stalking and stalking, attack defenseless domestic animals and eat them. For example, chickens, goats, rams, sheep, etc.
My life is also directly related to the animals of this squad. For example, a representative of the feline family lives in my house - the cat Vasya. Watching his behavior, I came to the conclusion that cats are excellent hunters, because they can perfectly disguise themselves and attack from shelter, hitting the victim with their agility by agility.
And now I would like to introduce you to my project, in which we will get acquainted in more detail with this view of the animal world.
Common signs of the detachment
 Animals belonging to the predatory order are distinguished among the remaining groups of mammals by an extraordinary variety of appearance, body size, biological characteristics, adaptations to the environment, ways of transportation, etc. Most predatory animals lead a terrestrial lifestyle, but certain species, like minks and otters are inhabitants of fresh water bodies, and sea otters are marine animals. Predators feed not only on meat, but also on insects, invertebrates, and even plant foods.
Animals belonging to the predatory order are distinguished among the remaining groups of mammals by an extraordinary variety of appearance, body size, biological characteristics, adaptations to the environment, ways of transportation, etc. Most predatory animals lead a terrestrial lifestyle, but certain species, like minks and otters are inhabitants of fresh water bodies, and sea otters are marine animals. Predators feed not only on meat, but also on insects, invertebrates, and even plant foods. The body length of predators varies from 14 cm to 3 m, weight from 100 g to 1000 kg. The shape of the body can be elongated, flexible, massive, sometimes awkward. Some animals have tall, slender limbs, many others have short, clumsy. On each limb there are at least four fingers, and in bears and dogs there are five of them. All predators have claws, especially sharp ones in cats, in which (except for the cheetah) they can be drawn. In contrast, in some species of otters and in a sea otter, the claws turned into a kind of nails. Most predators have a long, often fluffy tail, and only in bears, a large panda and some others it is small and hidden in fur. Representatives of two genera of raccoons and wyverns have a grasping tail. The outer auricles in most species of predators are well developed, pointed, in the fenech and large-eared foxes are unusually large, while in the Arctic fox, ermine, weasels and others are barely protruded from the surrounding fur, and in the sea otter are underdeveloped. All predatory animals have a well-developed hairline, diverse in density, length, splendor, and color. Many species have a mottled coloration of the fur. In some northern species, a seasonal color change is observed - whitening of fur in winter (weasel, ermine, arctic fox) or its significant brightening (polar wolf).
External and internal structure of predators
The number of teeth of predators varies from 28 to 48. Among them are well developed, more or less curved, pointed fangs. The last upper preroot and the first lower molar in most species have turned into special predatory teeth. But the incisors are small. The high level of nervous activity characteristic of predators is ensured by the great perfection of the brain. It has well-developed hemispheres with three grooves, numerous convolutions, large olfactory lobes. Of the structural features of the internal organs, a simple, gland-rich stomach can be noted. The intestinal length of carnivorous predatory species is relatively small. All predators, with the exception of hyenas, have a penis bone. Many species have well-developed anal glands, which emit a sharply smelling content, which serves to mark the territory, and sometimes (for a skunk) and to protect against enemies. The skin of predators is covered with hair. There are 2 types of wool - spine and undercoat.
Habitat
The vast majority of predatory animals leads a terrestrial lifestyle, inhabiting primarily forests, to a lesser extent - open spaces and mountains. Among forest predators, many climb trees well, but only some species of raccoon and civerora families are specially adapted for living in crowns. Some predators live near ponds, swim well and dive. Shelters of predatory animals are independently dug, sometimes very deep burrows, alien dwellings, as well as crevices of rocks, caves, niches among the roots of trees, hollows, piles of stones and windbreak, littered with snow in the North in winter. Often, one predator has several shelters, others manage with open dens and simple lying on the ground and in the snow.
Squad Families
The squad is predatory.
This family includes wolves, foxes, arctic foxes, dogs, jackals, coyotes and many others.
Feline Family (Felidae) . Medium and large animals. The body is slim and flexible. The head is round. Fangs are long, curved. Pads are developed on the fingers. Feline - of all carnivores, they are better suited to obtaining animal food mainly by way of guard, more rarely, by persecution. They feed on the meat of their victims. Among feline there are excellent runners. They are all finger-oriented. They eat only animal food. Active all year round. They live mainly alone or in families.
This family includes cats, leopards, lions, cheetahs, panthers and etc.
Family of BEARS (Ursidae). Bears are the largest of modern predatory animals. All animals of this family have a powerful body, many with a high withers; paws strong, with large claws, five-fingered, stop-walking; the tail is short, barely visible from the fur; the head is massive, with small eyes and ears. The coat is dense, uniformly dyed in black, brown or white, not changing seasonally.
This family includes brown, polar bears,
COUNTY family (). Small and medium-sized animals. The body is elongated, legs are short.
This family includes martens sables, ferrets
Findings:
In conclusion, I would like to draw a few conclusions. During work, I got acquainted with very interesting, diverse and informative information. While working on the project, I learned a lot about the life, meaning and structure of predators. The work was interesting, exciting, and most importantly productive!
List of used literature:
1. M.A. Kozlov, “Biology. Animals. ”Textbook for grades 7-8, Moscow“ Enlightenment ”, 1990, pp. 256
2. A.G. Bannikov, P.A. Genkel, “Plants and Animals” Children's Encyclopedia, Moscow “Pedagogy”, 1973, p. 447
3. L. Yakhnina, A. Zaitseva, “Ecology”, encyclopedia, “Rusich”, 1998, p. -151
4. A.S. Barkov, I.B. Shustova, “Big Atlas of animals”, “ROSMEN”, 1998, p. 67
5. www.floranimal.ru
X search teeth - these are four molars, characterized by size and sharp, cutting tubercles.
Ost - This is thick, long hair that protects the skin from damage.
Undercoat - This is a short, soft hair that retains body heat.
Propagate once a year, are highly fertile.
Foot climb - when walking, they rely on the entire foot.
